Afghan Authorities Accelerate Push for Road and Rail Projects
As the Taliban government pursues an assertive policy to enhance Afghanistan’s logistical infrastructure, interest in the country’s role as a southern transit hub is gaining momentum across West Asia.
As the Taliban government pursues an assertive policy to enhance Afghanistan’s logistical infrastructure, interest in the country’s role as a southern transit hub is gaining momentum across West Asia, facilitating the joint implementation of a wide range of new road and rail projects. Leading the charge is Uzbekistan, which has revived its ambitions through the Termez–Mazar-i-Sharif–Kabul–Peshawar railway—better known as the Kabul Corridor—positioning itself at the forefront of regional integration.
Meanwhile, Turkmenistan, backed by Kazakhstan, is advancing a parallel railway initiative through western Afghanistan to secure more direct access to Pakistan’s seaports. In a symbolic move, the foundation for the 22-kilometre Torghundi-Sanobar railway line was laid in September 2024, making a significant step towards reshaping regional connectivity.
The growing engagement between the Central Asian republics and Kabul in the development of transport infrastructure reflects a shared ambition to diversify foreign trade routes and establish more efficient supply chains to access the vast South Asian market. Alongside ongoing projects involving Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, and Kazakhstan, Afghan authorities have announced plans to construct the Mazar-i-Sharif–Herat–Kandahar railway. This line has the potential to become the shortest trade route between India and Russia, enabling New Delhi to build transport links with Afghanistan and Central Asia while bypassing Pakistan.
Even Iran, which remains the primary conduit linking Central Asia to the warm waters of the Indian Ocean, and, by extension, to global trade, is seeking stronger transport links with Afghanistan. Tehran is planning to launch two railway connections to Afghanistan simultaneously: the Khaf–Herat line in the north and the Zahedan–Zaranj line in the south-west. The railway from Khaf to Herat is nearly complete, and the Taliban intend to extend it to Mazar-i-Sharif, a key Afghan trade hub already connected to the Uzbek-built Hairatan–Mazar-i-Sharif railway (launched in 2011) and the planned Kabul Corridor. Integrating these routes could eventually allow Iran to reach the Wakhan Valley in Afghanistan’s Badakhshan province, which is the narrow strip of land separating Afghanistan from China.
Notably, during a Taliban delegation’s two-day visit to Tashkent in February 2025, Uzbek and Afghan authorities agreed to jointly implement the Mazar-i-Sharif-Herat railway route. According to the Afghan Deputy Prime Minister for Economic Affairs, Mullah Abdul Ghani Baradar Akhund, this project would expand Tashkent’s trade with South Asia, Iran, and China, reinforcing the idea that Tehran could utilise the Kabul Corridor to reach the borders of China’s Xinjiang region. Another potential route could see the Zahedan-Zaranj railway extended to Kandahar and Kabul with its subsequent link to the Wakhan Corridor.
In 2020, Iran began constructing the Chabahar–Zahedan railway line, with plans to extend it to Zaranj in Afghanistan’s border province of Nimroz and further onward to Dilaram and Kandahar. Engineering surveys have already been conducted on the Afghan side for the Zaranj–Kandahar railway, which could offer Tehran an alternative access route to Afghanistan beyond the Herat Road—bringing it one step closer to creating a new overland trade route to China.
Nevertheless, the prospect of reviving the Wakhan Corridor— an outcome eagerly anticipated by Tehran—remains uncertain. In 2024, Afghanistan’s Ministry of Rural Rehabilitation and Development announced the completion of gravel laying on a 50-kilometre stretch of the road. However, substantial investments are needed to turn the ancient route into a viable commercial transit point. The Taliban are striving for help from China, although Beijing has so far adopted a cautious, wait-and-see approach and is in no rush to open its arms to Afghanistan.
Despite this limited progress, Tehran appears unlikely to back down, particularly as it pursues other ambitious projects. One of these is the proposed Iran–Afghanistan–Tajikistan–Kyrgyzstan–China railway corridor, also known as the Five Nation Road.
Its initial section will be the Khaf-Herat railway, scheduled to begin full operations later this year. The route would continue through Sheberghan, Mazar-i-Sharif, Khulm, and Kunduz, ultimately reaching the Tajik border at the Sherkhan Bandar crossing. It would then stretch eastwards across Central Asia to Kashgar in western China, spanning an estimated 2,000 kilometres. In this context, the Taliban’s proposed Mazar-i-Sharif–Herat railway becomes a strategic segment of a broader transit route from Iran to China.
The creation of a Five Nation Transit Corridor could also benefit Turkmenistan, which has long pursued a railway link to Tajikistan via Afghanistan through the TAT project. This initiative emerged in 2013 amid rising tensions between Tashkent and Dushanbe over transit routes and the desire to bypass Uzbekistan.
Turkmenistan completed the first stage of the TAT railway in 2016, spanning from Atamurat (Kerki) through Ymamnazar to Akina. The Akina–Andkhoy segment followed in early 2021. However, the Taliban’s return to power in summer 2021 brought work to a halt, as regional actors reassessed the group’s stance on cross-border infrastructure and foreign engagement. Yet contrary to initial concerns, the new Afghan leadership has shown a pragmatic approach to regional connectivity.
In February 2025, Afghanistan and Turkmenistan agreed to carry out survey and design work for the 55-kilometre Andkhoy–Sheberghan railway line, a project first announced by the Taliban in 2024. Meanwhile, in July 2024, Tajikistan’s Ministry of Transport and the Korea International Cooperation Agency signed a protocol to develop a feasibility study for a 51-kilometre Jaloliddini-Balkhi–Panji Poyon railway, linking Tajikistan to the Afghan border. Both developments indicate a resumption of the TAT project, which could raise concerns in Uzbekistan, given its longstanding role as a key transit country for several of its neighbours’ access to global markets.
The development of trans-Afghan logistics infrastructure is also of growing interest to Russia, which sees the new corridors as a means of extending its flagship International North–South Transport Corridor (INSTC) to Pakistan.
A clear indication of this was the visit of a Russian delegation led by Security Council Secretary Sergei Shoigu to Kabul on 25 November 2024, during which the construction of the Trans-Afghan Railway was discussed. Following talks with the Taliban, Russian Deputy Prime Minister Alexei Overchuk stated that the Russian Federation considers this project as an integral component of the INSTC.
The Russian Ministry of Transport later announced that it would collaborate with Uzbekistan to prepare a feasibility study for a railway through Afghanistan, based on two agreed routes: Mazar-i-Sharif–Herat–Dilaram–Kandahar–Chaman and Termez–Naibabad–Logar–Kharlachi. But this announcement was not confirmed by Uzbekistan Railways.
Russian involvement in constructing both the western and eastern Afghan railway routes—starting from the borders with Turkmenistan and Uzbekistan, respectively—would allow Ashgabat and Tashkent to secure a share of cargo flows between Northern Eurasia to South Asia. Increased competition along these routes is likely to drive down the cost of transit transport over time.
The opening of new trade routes through Afghanistan presents significant opportunities for realising Central Asia’s economic and transport-transit potential. Several key factors should be considered when assessing further developments in this area.
One consideration is the potential reorientation of Uzbekistan towards the western Trans-Afghan railway route. The relative cost-effectiveness of the Kandahar Corridor, compared to the railway via Kabul, could serve as a catalyst for such a shift. Although the Mazar-i-Sharif-Herat-Kandahar-Chaman route (1,468 km) is longer than the Kabul Corridor (647 km), it offers advantages in terms of terrain and security. Additionally, the route can branch towards Iran through the border province of Nimroz in south-western Afghanistan, providing a valuable strategic link for future transport corridors.
Another important factor is the growing security risks in Pakistan, coupled with increasing tensions in Afghan-Pakistani relations. These dynamics may prompt Tashkent and its external partners to reconsider their preferences on the trans-Afghan track, favouring the Kandahar Corridor instead. In this context, prioritising a transit route that connects to the southern regions of Pakistan—those closest to the ocean—would be more appropriate.
Given the growing significance of Afghan transit in transregional logistics, Central Asian countries will need to balance the interests of all stakeholders to prevent the emergence of intensified geopolitical rivalries along these evolving trade corridors. Harmonisation of the trans-Afghan routes currently under development appears to be both the most likely and most favourable scenario for the future. In such a case, the key stakeholders, particularly Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan, could pool their resources to establish a unified transregional railway corridor through Afghanistan.
This collaborative approach would enhance the prospects for attracting external investment and accelerating project implementation. Moreover, a consolidated approach is vital for strengthening the region's role in shaping the emerging architecture of trans-Afghan connectivity. If done successfully, Afghanistan could gain a genuine opportunity to position itself as a new transit hub at the heart of Eurasia.
Photo: Asian Development Bank
How Trump Can Strike Gold for America in Iran
Trump loves gold. If he remains pragmatic and focused when it comes to Iran, he could strike gold in several ways.
There is a curious line in the Omani statement issued following the latest round of nuclear negotiations between the United States and Iran in Rome, which concluded on Saturday. The statement declares that Iran’s foreign minister, Abbas Araghchi, and Trump’s special envoy, Steve Witkoff aim to “seal a fair, enduring and binding deal which will ensure Iran [is] completely free of nuclear weapons and sanctions.” The sentence is striking because it implies that the US is considering lifting primary as well as secondary sanctions, something that goes beyond the sanctions relief provided under the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA).
Is this just a case of sloppy drafting by the usually diligent Omani mediators? Well, the Wall Street Journal has reported that Iran has offered Trump a high-level meeting in Washington if a deal can be reached, something that would be difficult to imagine if Iran were to remain under an effective US embargo after the deal’s implementation.
Iranian officials have certainly been touting the possible economic benefits of a renewed nuclear deal for the US. When Araghchi described Iran as a “trillion-dollar opportunity” in a recent op-ed, he had one investor in mind—Donald Trump. As the US and Iran take further steps in the nuclear negotiations, Iranian officials have been eager to make clear that agreeing a new nuclear deal, which would at a minimum require the US to lift secondary sanctions on Iran, could prove a boon not just for the Iranian economy but also for the American economy. To emphasize the point, Iranian President Masoud Pezeshkian even announced that Iran’s Supreme Leader, Ali Khamenei, has “no objection” to American investment in Iran—an attempt to conjure a positive atmosphere ahead of the first round of indirect talks between Araghchi and Witkoff in Muscat.
It remains unclear whether the Trump administration will be able to achieve a viable deal with Iran. The administration’s position on key issues, such as Iran’s ability to maintain uranium enrichment, remains ambiguous, and there is significant distrust on both sides. If the negotiations are to succeed, they will need to find a win-win formula—hence the Iranian insistence on portraying any new agreement as not just a nuclear deal, but also a business deal. Iranian leaders have been watching Trump’s recent moves—his aggressive use of tariffs, his imposition of a critical mineral deal on Ukraine—and they have smartly concluded that Trump cares more about American enrichment than Iranian enrichment.
Is Iran really open for American businesses? The answer is yes, especially if Iranian and American policymakers make the restoration of their bilateral economic relationship a priority alongside restoration of a nuclear deal. Lifting primary sanctions would have a dramatic impact on US-Iran economic relations. But even if those sanctions remain in place, there are ways in which the US and Iran can structure their bilateral economic relations, opening new channels for trade and investment.
The heyday of US-Iran economic relations dates to the 1960s and 1970s. American firms like General Electric, General Motors, and DuPont played a central role in Iran’s industrialization, helping the country’s oil and manufacturing sectors achieve global prominence. Consumer brands like Gillette, Colgate, and Coca‐Cola were beloved by Iranian households.
The 1979 Islamic Revolution brought an end to diplomatic relations between the United States and Iran. That year, the US imposed sanctions targeting the Iranian economy for the first time. The New York Times reported on the exodus of American firms from Iran with a report titled, “Iranian Festival Is Over For American Business.”
But the change in Iran’s geopolitical and ideological orientation did not change a basic economic reality—the 1990s were an era of unipolarity and it was prudent to do business with the world’s largest economy. Iranian President Hashemi Rafsanjani tried to rekindle economic relations with the United States, believing that higher levels of trade and investment would help restore relations between the two countries. He offered the Islamic Republic’s first post-revolution oil field development contract to ConocoPhillips, maneuvering around domestic opposition to the deal. But the deal was blocked by the Clinton administration, which subsequently tightened US sanctions on Iran. The episode served as an early warning that the hardliners most capable of thwarting diplomacy were those in Washington, not Tehran.
American firms maintained a small presence in Iran in the early 2000s while European firms emerged as Iran’s preferred partners. The Europeans established joint ventures and wholly owned subsidiaries in the country and did brisk business. French oil giant Total took over the deal first offered to Conoco-Philips. French and German automakers retooled the Iranian automotive industry, making it one of the largest in the world. European brands flew off supermarket shelves as Iranian household purchasing power recovered on the back of 16 consecutive years of economic growth.
Iran’s economy hit a stumbling block in 2012 as the international community tightened international sanctions—with the measures hinging on President Obama’s unprecedented package of financial sanctions imposed at the start of that year. Subsequent nuclear negotiations focused on restoring Iran’s trade and investment ties with Europe, but the Obama administration did understand that enabling more trade between the US and Iran could create broader constituencies in Washington who backed the JCPOA, which was implemented in January 2016.
While primary sanctions remained in place after implementation of the deal, the JCPOA opened three pathways for US business that wished to pursue opportunities in Iran. First, certain US companies were able to apply for specific licenses from the Office of Foreign Asset Control (OFAC), part of the Treasury Department, permitting deals that would otherwise be blocked by primary or secondary sanctions. Among the contracts licensed in this way were the roughly $20 billion in deals Boeing negotiated for the sale of commercial aircraft to Iranian airlines, contracts that became symbolic of the nuclear agreement’s broader potential.
Many American companies took advantage of General License H, which stipulated that non-US subsidiaries of US companies could broadly engage with the Iranian economy. For example, Procter & Gamble, which ran its Iran operation out of its Swiss subsidiary, rapidly re-entered the Iranian market, where it could reliably generate over $100 million in annual revenue. American technology companies took advantage of a similar license called General License D-1 to export digital services to Iranian users.
Finally, American companies were even able to export to directly Iran without relying on a licensing regime if their sales were consistent with longstanding exemptions for humanitarian trade. Medical device companies like GE Healthcare and Baxter enjoyed bumper sales to Iranian hospitals. Pharmaceutical giants like Eli Lilly and Pfizer also increased sales, taking advantage of an opening in financial and logistics channels. American commodities giants like Cargill and Bunge sold wheat, sugar, and soybeans to Iranian buyers, including crops grown on American farms.
In short, American companies were making inroads in Iran as recently as eight years ago. It was President Trump’s unilateral decision to exit the Iran nuclear deal and reimpose secondary sanctions that brought an end to these renewed economic relations, leading to the cancellation of billions of dollars of contracts.
Immediately after Trump’s election, Boeing began to lobby the administration not to withdraw from the JCPOA—something Trump had promised to do on the campaign trail. The planemaker argued that the huge Iran contracts supported “tens of thousands of US jobs” and tried to appeal to Trump’s interest in reviving American industry. The appeals did not work. But it is easy to imagine Trump grasping benefits of a massive Boeing deal at this juncture, given the how darling of American industry has lost its shine. Demand for aircraft in Iran could also help compensate for the impact of Trump’s new China trade war on Boeing. Earlier this week, China banned the purchased of American aircraft, putting hundreds of Boeing orders in doubt.
The JCPOA experience makes clear that there was no prohibition in Iran against doing business with US companies. In fact, relations with the US nosedived after Trump’s abrogation of the nuclear deal, but some direct economic links persisted. Iran offered a lifeline for many American soybean farmers who were hammered during Trump’s first trade war with China. When China retaliated by ending the import of American soybeans, crashing the price, Bunge stepped in, delivering multiple cargoes of American-grown soybeans to Iran, even as Trump brought secondary sanctions back in force.
Clearly, a new nuclear deal could rekindle US-Iran economic relations. But the rebound in trade and investment will likely be modest unless there is a concerted effort by both the American and Iranian governments to make deeper economic relations a cornerstone of a new deal—especially if primary sanctions remain in force. Most American firms will be wary about entering the Iranian market given the inherent concerns that any deal between the two countries could break down, leading Trump to reimpose sanctions once again. Companies are also increasingly risk averse in the face of a volatile global economy. Leaving it to the private sector to singlehandedly realize the economic opportunities of the nuclear deal, the strategy taken back in 2016, is unlikely to work. Bilateral trade may rise from its low base, but investment will not materialize given risk perceptions, meaning there will be little in the way of shared incentives to bind the US and Iran together. A more structured plan for cooperation is needed.
Iranian negotiators are seeking structured cooperation, although their vision remains somewhat ill-defined. Reprising a demand from the talks that were undertaken with the Biden administration, Iranian negotiators continue to target some form of “guarantees” that would ensure the US cannot easily and costlessly withdraw from the nuclear deal while Iran remains in compliance with its obligations. Political and legal guarantees will have little weight. But deeper US-Iran economic cooperation can act as a kind of “technical guarantee” that serves to increase the credibility of the long-term commitments enshrined in any new nuclear deal.
Trump’s turn towards a decidedly “America First” economic policy might actually help Iran as it tries to find a win-win formula for economic cooperation that goes beyond increased purchases of American consumer goods, pharmaceutical products, and agricultural commodities. As economist Djavad Salehi-Isfahani has recently detailed in a review of investment data, Iran desperately needs to renew its capital stock and reverse a decade of technological regression. Meanwhile, the US is trying to rekindle domestic manufacturing of capital goods. The interests align nicely.
The economic commitments related to any new US-Iran nuclear deal should be structured to enable Iranian industrial giants to make major purchases of American-made capital goods—machinery, equipment, aircraft, and vehicles.
Iran’s capital stock is primarily European and was installed around 20 years ago, when European firms were making major investments in the country. But a significant portion of this machinery remains American in origin or design—a reflection of the fact that large parts of Iran’s industrial sectors have not been updated since the 1970s. Many turbines spinning in Iranian power plants and diesel locomotives chugging on Iranian rails are based on GE designs. Many drill heads used to bore oil wells are derivatives of Schlumberger designs—the Texas company’s former Iran subsidiary lives on. Another former American subsidiary, Iran Combine Manufacturing Company, was once called “Iran John Deere.” The company continues to produce trademark green and yellow tractors and combine harvesters—using American designs from 50 years ago. American engineers will find familiar technologies in use at Iranian industrial plants. Renovating and upgrading these facilities will be straightforward, especially given the incredible acumen of Iranian industrial engineers and technicians who will be eager partners.
Importantly, a surprisingly small portion of Iran’s capital stock is Chinese. Chinese exports of capital goods to Iran totaled $6 billion in 2023. But this is the same level as achieved in 2017, the last year that Iran enjoyed sanctions relief. Meanwhile, Chinese investment in Iran has languished under sanctions, plateauing since 2014. There are no major Chinese manufacturing investments in the country and Iran has not been able to substitute the loss of its European industrial partners with Chinese partners. That leaves a uniquely large and open market for American exporters—perhaps the last major economy in the world where the US could reasonably overtake China as an industrial partner.
Given the aligned interests of their respective industrial policies, the US and Iran should think ambitiously about the scope of their economic relations. Iranian firms will be eager customers for new machinery and equipment. Crucially, this kind of trade does not make Iran dependent on the US. Rather, it restores the strength and resilience of the Iranian industrial sector. Once capital goods are installed, they can last for decades—a kind of guarantee that the benefits of a US-Iran deal will last.
Finally, Iranian purchases of American equipment must be financed by American banks. This will make it more likely that the financial logjams associated with JCPOA sanctions relief will be solved. If US banks do business with Iran on Trump’s instructions, global banks will follow. Notably, Trump’s efforts to revitalize the Export-Import Bank could give American exporters access to crucial export credit, insurance, and guarantees.
Trump loves gold. If he remains pragmatic and focused when it comes to Iran, he could strike gold in several ways. He could forge the kind of nuclear deal Thomas Pickering once called the “gold standard for non-proliferation agreements,” once again subjecting Iran to the strictest IAEA verification regime ever devised. He could earn billions in export revenue for the US—and given the US is unlikely to import much Iranian oil—generate a rare trade surplus with a country that is poised to return to its position as one of the twenty largest economies in the world. Finally, if Trump is ambitious and if Iran’s leaders are courageous, he could finally earn the gold medal he has always wanted—a Nobel Prize.
Photo: The White House
To Avoid a Currency Crunch, Iranian Automakers Are Trading Nuts for Bolts
The outlook for the Iranian automotive industry looked dire until Iranian automakers stumbled upon an unexpected solution.
In a typical year, 10 out of every 100 dollars that Iran spends on Chinese goods goes towards car parts. While the China-Iran trade relationship has languished under sanctions, China has remained a critical supplier for the Iranian automotive industry, which continues to produce over one million automobiles annually.
But over the last year, Iranian automakers have struggled to keep the parts flowing. Parts imports from China totalled $653 million in 2024, a precipitous 43 percent decline when compared to the previous year.
The fall in imports has led to a shortage of car parts in Iran, with consumers facing long wait times and soaring prices. The impact has been most acute for Iran’s private sector automakers, who mainly assemble cars using complete knock-down kits imported from China. Whilst Iran’s state-owned automakers are supported by a large ecosystem of domestic parts manufacturers, private-sector automakers remain heavily dependent on Chinese imports to keep their customers’ cars on the road.
The main cause for declining imports has been a lack of access to foreign currency, a consequence of US secondary sanctions restricting Iran’s banking relations with China. Even though Iranian oil exports to China have rebounded in recent years, they have not alleviated Iran’s foreign exchange crisis. Iranian companies seeking to import goods from China have struggled to receive timely allocations of renminbi through the Central Bank of Iran’s foreign exchange market.
As the currency bottleneck grew tighter over the course of 2024, imports continued to fall, and by the summer, the situation was being described as a “crisis.” In September, imports of car parts from China hit a nadir, with just $26 million worth of parts departing for Iran that month—a 65 percent year-on-year drop.
The outlook for the Iranian automotive industry looked dire until Iranian automakers stumbled upon an unexpected solution. In need of a new source of renminbi, many Iranian automotive firms turned to the pistachio business. Like oil, pistachios are a valuable commodity in which Iran is a world-leading producer. Unlike oil, pistachios are exempt from secondary sanctions.
Iranian automotive companies began purchasing pistachios from growers and leveraging their logistics networks to ship them to China. As a result, Iranian pistachio exports to China quickly surged to historic highs, enabling a modest recovery in car parts imports. In the last six months of 2024, Iran exported $195 million worth of in-shell pistachios to China—more than 2.5 times the volume achieved in the same period in 2023.
Pistachio growers and wholesalers, however, were not happy. Many Iranian pistachio wholesalers had given up on exports—leaving the Chinese market open to new entrants. The requirement to repatriate export earnings through the centralised foreign exchange market made margins unattractive for many agricultural firms. But for automotive companies, profit from pistachio sales was never the primary objective. Selling nuts provided a quick way for them to earn the foreign currency they needed to import car parts, which could then be resold in Iran at much higher margins. By October, industry leaders were complaining of “chaos in Iran's pistachio trade” as automakers turned into “inefficient competitors of Iran's real pistachio exporters.”
Pistachio exporters are reportedly seeking an understanding with the automakers who edged onto their turf. They plan to sell their foreign currency to automakers at a rate agreed with the supervision of the Central Bank of Iran, ensuring sufficient margins to incentivise them to prioritise exports once again.
Sanctions have not crushed the Iranian economy, but they have made pistachios more valuable than oil, forced importers to become exporters, and pushed automakers into competition with farmers. In adapting to sanctions pressure, the solution to one crisis can beget another, leaving a country trading nuts for bolts.
Photo: IRNA
Facing New Alignments, Iran and Tajikistan Relaunch Partnership
Iran and Tajikistan may share the same spirit, but they do not yet appear to share the same interests.
Earlier this month, Mahmoud Khosravi Vafa, the head of Iran’s National Olympic Committee, met with Shamsullo Sohibov, Vice-President of Tajikistan’s National Olympic Committee, to discuss improving sports cooperation. The meeting was more than just a consultation between two bureaucrats, it marked the latest step in the recent rekindling of the relationship between Iran and Tajikistan, two countries with deep linguistic and cultural ties.
Once described as “one spirit in two bodies" by the ex-president of Iran, Mahmoud Ahmadinejad, the relationship between Iran and Tajikistan underwent an unexpected breakdown in the mid-2010s. Now, as Iran continues to struggle under Western sanctions, contend with a new hostile US administration, and adapt to its weakened position in the Middle East, it is again turning east. For its part, Tajikistan is pursuing a multi-vector foreign policy, diversifying relations with as many international partners as possible to secure economic and political assistance.
After the collapse of the Soviet Union, Iran was the first country to recognize Tajikistan’s independence and establish an embassy in the capital, Dushanbe. Tajikistan reciprocated by opening one of its first foreign embassies in Tehran in 1995. Subsequently, during the civil war in Tajikistan between 1992 and 1997, Iran was part of a foreign coalition that helped mediate the conflict. In this period, Tehran also cautiously supported the Islamic opposition to the current regime in Dushanbe.
After Tajikistan’s civil war ended, Iran made lofty pronouncements of friendship but took few concrete steps towards collaboration. But following the September 11 attacks and the deterioration of Western economic and political relations with the Middle East and its surrounding countries, Iran began to reinvigorate foreign policy towards Tajikistan to compete with the growing Western influence in West Asia.
During two terms in office, former Iranian President Mohammed Khatami committed to funding large-scale infrastructure projects in Tajikistan, such as the strategically significant Anzob Tunnel and Sangtuda-2 hydropower plant. Total trade between the countries tripled from $40 million in 2000 to $140 million in 2007. However, the relationship rested primarily on economic diplomacy; politically, Iran was more focused on counterbalancing the US presence in Afghanistan and on deferring to Russian decisions in Central Asia due to Russia’s support for Iran’s nuclear program.
Mahmoud Ahmadinejad’s presidency led to a complete reorientation of Iran’s foreign policy towards its eastern neighbors and against the Western agenda in the region. While in office, Ahmadinejad met annually with Tajik President Emomali Rahmon, whose government remained quietly wary of Iran, given its role in the Tajik civil war, the accelerating nuclear program, and the desire to avoid being dragged into Iran’s conflicts with Israel and the US. Prioritization of economic diplomacy over politics remained the foundation of Dushanbe’s foreign policy, allowing it more flexibility in playing its allies against each other and extracting more concessions. However, at the time, Tajikistan accepted Ahmadinejad’s overtures, lacking better options in the face of minimal Western economic assistance.
Nonetheless, Iran’s investments proved to be problematic. The Anzob Tunnel was shoddily and hastily finished just in time for President Ahmadinejad’s first visit to Tajikistan in 2006, and poorly maintained even a decade after its construction. Moreover, the construction of Sangtuda-2 was finalized only in 2013—significantly behind schedule—and the power plant was shut down briefly over Tehran’s concerns that Dushanbe could not eventually repay the construction loan. Finally, the US government turned its attention to Iran’s use of Tajikistan’s then largely unregulated financial sector to circumvent Western sanctions and to launder money for Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corp (IRGC), as exemplified in the case of Iranian businessman Babak Zanjani.
Zanjani, who owned a bank, an airline, a taxi service, and a bus terminal in Tajikistan, was sentenced to death in Iran for allegedly embezzling over $2.7 billion from the country’s state-owned oil industry. His foreign investments were expected to be seized and returned to Iran’s government. But the Tajik authorities denied having any of Zanjani’s assets, angering counterparts in Iran.
In December 2015, Iran, which supported Tajikistan’s moderate Islamic Renaissance Party (IRPT) during the country’s civil war, invited its leader Muhidin Kabiri to an Islamic conference where he was warmly welcomed by the Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei. The government of Tajikistan, which had accused IRPT of an alleged coup attempt just a few months prior, arrested several of its members. Moreover, the Tajik authorities designated the only religious political party in Central Asia a terrorist organization, immediately issuing a note of protest to Iran. The Foreign Affairs Ministry of Tajikistan angrily summoned the Iranian ambassador. The head of the Council of Ulema of Tajikistan described Iran's invitation of Muhidin Kabiri as "abetting terrorism."
Dushanbe’s reaction echoed not only the tensions of the civil war but also the country’s deep commitment to secular government, a legacy of the Soviet Union. The Tajik government distinguishes between traditional Islam, which it supports as part of Tajik social life and culture, and political Islam, which it views as a potential threat to state power. Dushanbe’s secular stance allows it to play up the threat of religious extremism to crack down on political rights domestically. The avowed opposition to political Islam has also allowed the country to seek Western aid–a strategy that always stood in conflict with theocratic Iran’s politics.
In response to Iran’s reception of Kabiri, Tajikistan halted the imports of Iranian food products, including poultry, cooking oil, and tea, for the alleged poor quality of these products, as well as a lack of compliance with Tajikistan’s language regulations for product labels. In July 2016, the Transportation Ministry of Tajikistan publicly accused Tehran of violating the terms of the contract to build a key regional railway. Later, the authorities suspended the Tajik branch of the Imam Khomeini Relief Committee, a charity organization supported by the government of Iran.
Arguably, the most significant blow to the countries’ relationship landed in August 2017. In a 45-minute documentary aired on Tajik state television, the Internal Affairs Ministry accused Tehran of fomenting the civil war in Tajikistan, providing financial assistance to the now-pariah IRPT, and training Islamist militants on Iranian soil to then be sent back to Tajikistan to carry out political assassinations—claims the government of Iran vehemently denied.
At the time, it seemed as though the only pan-Persian alliance in the region was over. Yet the sudden American withdrawal in May 2018 from the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action under President Trump once again highlighted Iran’s urgent need to continue building relationships with its eastern neighbors. Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei has repeatedly emphasized that Iran must “look to the East” for strategic allies who can help Iran resist Western pressure and overcome the banking and trade issues brought on by Western sanctions.
Thus, in 2019, Tehran and Dushanbe resumed communications. The volume of bilateral trade rose from around $55 million in 2020 to $121 million in the following year. Former Iranian president Hassan Rouhani visited Dushanbe in June 2019. In September 2021, the late Iranian president Ebrahim Raisi made Dushanbe the destination in his first foreign trip.
In May 2022, Iran inaugurated a drone production factory in Tajikistan, the first such facility that Iran has built in a foreign country. The factory builds and exports Ababil-2—a reconnaissance and combat drone that has been widely used by Russia in Ukraine—and represents not only Iran’s resumed security cooperation with Tajikistan but also attempts to counter its regional rivals’ influence in the country. This comes in response to Saudi Arabia taking advantage of the preceding period of ruptured relations between Iran and Tajikistan. During this time, Saudi Arabia invested in several economic and development projects in Tajikistan, pure geopolitical opportunism from Riyadh seeking to deprive Tehran’s position as a key ally and investor in Tajikistan. Iran’s drone factory is also an attempt to outrun both Turkiye, who reportedly sold its Bayraktar TB2 drones to Tajikistan in April 2022 during a brewing border conflict with Kyrgyzstan, and Israel, who regularly attacks Iran’s domestic drone-producing capabilities but will likely avoid doing so outside of Iran’s borders.
A few months later, in September 2022, Iran signed a memorandum of accession to the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) at the organization’s summit in Samarkand, Uzbekistan, becoming a full member in July 2023— a development that Russia and China strongly favored. Soon after, President Rahmon and President Raisi held talks on the margins of the 78th session of the United Nations General Assembly, where they discussed further expansion of bilateral cooperation. A flurry of high-level visits and signed agreements followed, including a historic establishment of a visa-free regime between the countries in November 2023.
The relationship between the two countries reached a new high in January 2025 during President Masoud Pezeshkian’s three-day visit to Dushanbe. Pezeshkian was warmly received as the guest of honor at the Tajikistan-Iran Trade, Economic Investment, and Tourism Forum. The two sides signed two dozen agreements on security, combatting drug trafficking and corruption, simplifying trade and customs, and improving transportation and education links. But while President Pezeshkian spoke of discussions between the sides covering the situation in Afghanistan and the war in Gaza, President Rahmon of Tajikistan emphasized developing cooperation in mining, pharmaceutical, industrial, and agricultural sectors, a reflection of Dushanbe’s continued desire to avoid controversial political topics and stick to economic and cultural collaboration.
Notably, the two presidents reopened the Institute of Tajik-Persian Culture in Dushanbe, which had been shut in the mid-2010s during the nadir in bilateral relations. President Pezeshkian also laid a wreath at the statue of Ismoil Somoni–a significant figure in Persian culture and history–and visited the Avicenna Tajik State Medical University, where he received an honorary professorship. The concluding government statements called on both sides “to find new and profitable ways of cooperation.”
The rekindling of the partnership between Iran and Tajikistan benefits both sides. Iran gains access to a largely untapped, albeit minor, market for its exports and diversifies its trade relations, allowing it more flexibility in the face of Western sanctions on Tehran and Moscow. A presence in Tajikistan brings Iran even closer to Russia and China, the two major geopolitical players in Central Asia, and provides Iranian leaders another avenue for security collaboration on Afghanistan. Finally, a foothold in Tajikistan allows Iran to counter the growing influence of Saudi Arabia and Turkiye in Central Asia after major losses in its political weight in the Middle East since 2024.
For Tajikistan, Iran is another source of foreign direct investment and a minor opportunity to ease its labor migration, trade, and economic assistance dependence on China and Russia, especially as the war in Ukraine and its fallout drag into its fourth year. Access to Iran’s regional transportation links and especially its security capabilities is another important consideration as Tajik authorities prepare for a long-awaited presidential transition. As President Rahmon prepares to transfer power to his son Rustam, his regime is looking for as many allies as possible to ensure stability during the transition.
Rekindling ties with Iran has its benefits. But it will also force Tajikistan into an old dance of balancing Iran’s internal and external politics with its own relationship to political Islam and its desire to stay neutral on the world stage. The two countries may share the same spirit, but they do not yet appear to share the same interests.
Photo: IRNA
The Job of Iran's Central Bank Governor Just Got Harder
If the free market exchange rate reflects the mood of Iran’s economy, the commercial exchange rate measures its pulse.
Last Friday, Iran’s Supreme Leader, Ali Khamenei, declared that negotiations with the United States were “not smart, wise, or honourable.” Addressing an audience of Iranian military brass, Khamenei did not explicitly rule out negotiations. But his tone made it clear that Iran was not about to begin talks with the Americans, despite American President Donald Trump stating just two days earlier that he wishes to start working on a nuclear deal with Iran “immediately.”
As is the case in sanctioned economies, when hopes deflate, prices inflate. Within the few days following Khamenei’s speech, the dollar appreciated nearly 7 percent against the Iranian rial, pushing the free-market exchange rate towards the threshold of 1 million rials to the dollar.
The free market accounts for a very small proportion of Iran’s multi-faceted foreign exchange market, generally reflecting the prices available to individuals purchasing physical bills at exchange bureaus. The free market dollar is the dollar that ordinary Iranians use to protect their savings in the face of chronic inflation (dollars stuffed under the mattress, so to speak) or to take their wealth abroad (dollars hidden in a briefcase, so to speak). These limited uses explain why the price of the free market dollar is such an important signal in the Iranian economy: it is the country’s highest-frequency measure of economic sentiments.
In this respect, Khamenei’s speech appears to have gifted Trump the first victory of his renewed “maximum pressure” policy. Despite Trump indicating he was “unhappy” to sign the presidential memo which directed his cabinet to increase pressure on Iran—and despite the limited scope and impact of his only enforcement action so far, the designation of three oil tankers—the rial plummeted against the dollar. Sometimes maximum pressure is self-inflicted.
Now that Iranian leaders appear to have rejected the opportunity to negotiate with Trump, at least for now, the question becomes whether maximum pressure policies will begin to have more than psychological impacts for Iran’s economy.
This question can be answered by monitoring the indicator that really matters for Iran’s economy— the commercial foreign exchange rate. Until recently, this was called the NIMA rate. The NIMA foreign exchange market was a centralized electronic system established by the Central Bank of Iran in 2018 to streamline the purchase and sale of foreign exchange among Iranian companies. The commercial exchange rate has been notably stable in recent weeks, showing little movement after Trump signed his presidential memo or after Khamenei declared that negotiating with the United States is “not smart.” This is not because Iran’s central bankers have managed to inure the commercial exchange rate to psychological impacts—it is because the impact was preempted in December.
The NIMA rate began to slide in the days after Trump’s election victory on November 4, 2024. This may indicate that, like in the free market, Trump’s victory spurred more demand for hard currency. Iranian companies, anticipating the return of maximum pressure, may have sought to import more goods and build-up inventories in order to mitigate future disruptions in their supply chains. Though, it is also possible that the election outcome led to a change in foreign exchange supply. For example, financial institutions facilitating Iran’s access to hard currency may have grown wary of future sanctions enforcement and could have begun to throttle payments flowing from customers to Iranian exporters. Whatever the reason, the commercial exchange rate was rising at a steady clip.
By mid-December, as rolling blackouts began to hit Tehran, the Central Bank made a dramatic move to devalue the rial. Between December 12 and December 16, the dollar price rose nearly 10 percent—the sharpest such increase since the NIMA rate was established. On December 14, the Central Bank issued an announcement about the new price-level and a plan to restructure the centralized foreign exchange market under the Iran Currency and Gold Exchange Center. Central bank governor Mohammad Reza Farzin, like his predecessors, has instituted new rules and names for Iran’s multi-level foreign exchange market; the aim is for these largely superficial changes to help the central bank manage the largely intractable structural imbalances of the foreign exchange market.
The central bank aims to encourage Iran’s major exporters, such as firms exporting petrochemical products and steel, to sell their foreign exchange earnings through the new Iranian Commercial Foreign Exchange Market. From the outset, Iran’s major exporters have been reluctant to supply the central bank’s foreign exchange market, despite regulations mandating them to repatriate foreign exchange earnings. Managers at these firms who had the political weight to ignore regulations have known that, in an environment where the rial was expected to continually weaken, holding onto dollars was a smart bet.
By allowing a sudden devaluation of the rial in December, the central bank made a major concession to the major exporters. The move may help the bank keep the foreign exchange market supplied with dollars and euros, but it fails to address the fundamental issue which is found on the other side of the ledger—there is no underlying demand for rials given the dim prospects for the Iranian economy.
It is yet to be determined what “maximum pressure” will mean during the second Trump term. Unlike in the first term, there is no Mike Pompeo and Brian Hook to lead the pressure campaign. Plus, little had to be done to restore maximum pressure, as the new presidential memo set out, given that the Biden administration had never rolled back the sanctions imposed during Trump’s first term.
Still, if Trump decides he has been jilted by the Iranians, he could take a more forceful approach to maximum pressure. Any such shift in rhetoric will no doubt push the free-market exchange rate to new highs. The real indicator of whether maximum pressure is hitting Iran’s economy will be the movement of the commercial foreign exchange rate. If the free market rate reflects the mood of Iran’s economy, the commercial rate measures its pulse.
Photo: IRNA
Iranian Architects Are Reshaping Their Country, Visually and Politically
Amidst recent years of social and political turmoil in Iran, a blossoming architectural scene is ever-present and defiant.
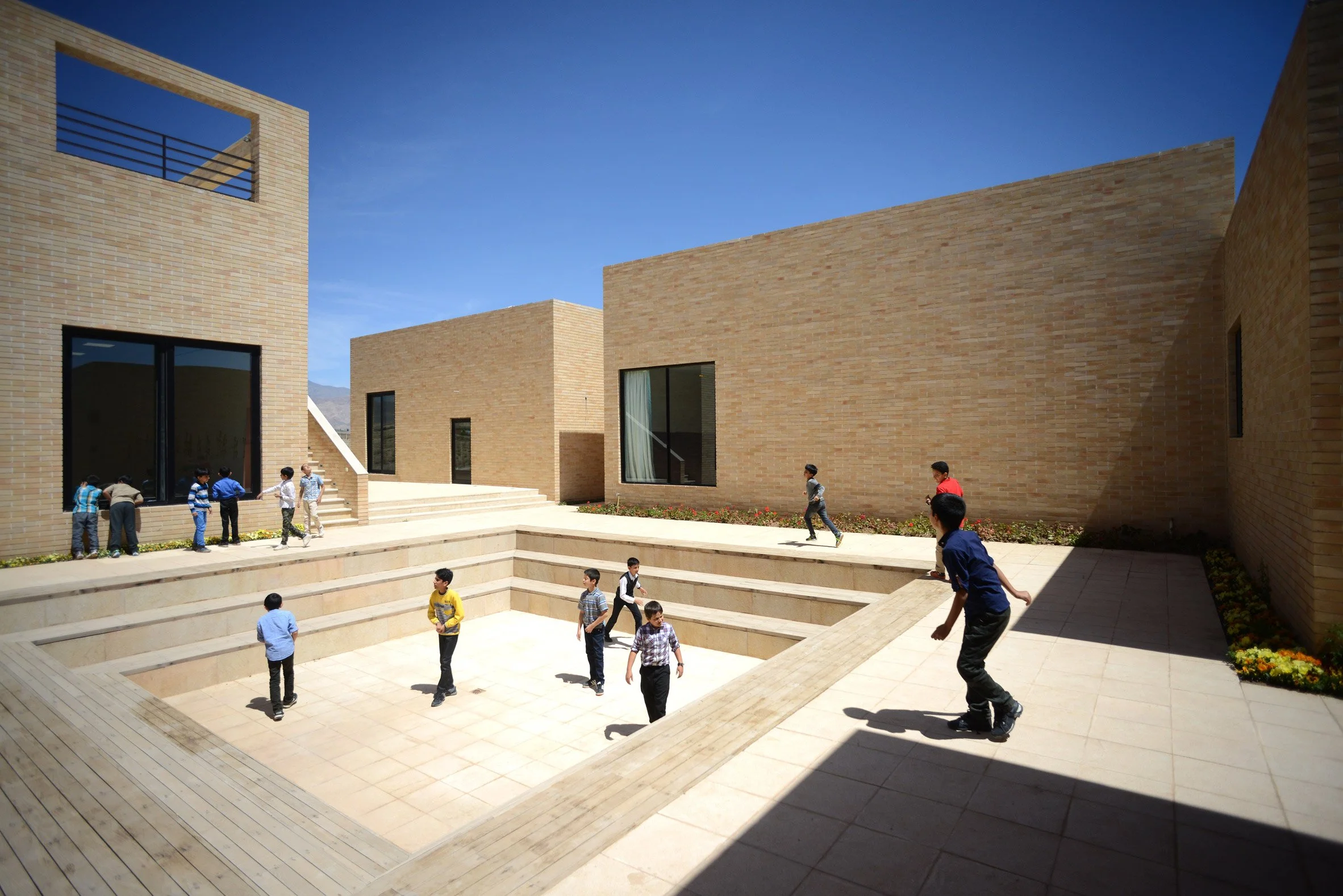
In a busy intersection in Iran’s capital city, Tehran, there is a "deceptively simple" metro station. The structure is meticulously constructed of up to 300,000 traditional bricks—a major collaboration between the station’s architects and local artisans.
Having secured the commission for the station at a time of significant protests in Iran, KA Architecture Studio wanted to recognise how public spaces “are the place of conflict in the metropolis of Tehran between the government and the people.” Such statements reflect the growing political significance that Iranian architects ascribe to their work, even when working on commissions from the government.
By placing projects like the Jahad Metro Plaza at arterial points of the city, architects in Iran are redefining the way public areas are used and determining points of congregation. In turn, their design choices spark discussion around the social and political significance of architecture beyond mere aesthetics.
Amidst recent years of social and political turmoil in Iran, a blossoming architectural scene is ever-present and defiant. Cropping up across major metropolises like Tehran and Mashhad and smaller cities like Ahvaz and Kelarabad, are new and intriguing structures, including luxury glass apartment buildings, eco-resorts with integrated mazes, colourful domed retreats, and geometric complexes. Through their ambitious designs, the structures being introduced to Iran’s cityscapes and landscapes challenge the view of Iran as a country without prospects.
These new buildings embody a cultural shift, in which features like open facades and glass walls take on a political significance. In a recent op-ed, Tehran-based correspondent Najmeh Bozorgmehr described how windows and balconies were once simply functional elements of homes in Tehran—“used for drying laundry or storing seasonal fruits and vegetables.” But today, the enlargement of open spaces in the home and the adoption of glass facades are indicative of a slow transition away from cloistered private spaces and towards an assertion of transparency and personal freedom.
While Iran’s wave of progressive architecture is growing, the completed projects vary in their accessibility to communities across Iran. Some cater to the ultra-rich, others seek to tie in varying strands of society. What can be said about either type of project is that they both strive to address qualms about Iran’s sociopolitical condition, while also attempting to invigorate a new wave of artistry, celebrate and interpret cultural heritage, and encourage a sense of community.
Historically, architects in Iran had to mask the political implications of their field. In a notable example, Architecture Magazine, long a leading publication for Iranian architects, did not “want to have the slightest conflict with the world of politics," according to one historian. Ambivalence was chosen to ensure the “survival of the architectural profession as an independent practice, on the one hand guaranteed [architects’] livelihood[s] and on the other was of great importance for the government's ‘nation-building’” objectives. But this cautious approach faded in the following decades, given that the architectural profession, like everything else in Iran for that matter, was clearly entangled with the political circumstances of the country. In 2022, during the aftermath of the arrest and death of Mahsa Amini while in the custody of the morality police, many architectural studios halted operations in solidarity and emphasised their commitment to the people.
Notably, many talented Iranian architects choose to remain in Iran despite the limitations politics may pose for their career—a decision that may be difficult to understand given the extent of brain drain plaguing other industries in the country. Mainly driven by political repression and, in turn, isolation from the global economy, young, highly-skilled Iranians are increasingly fleeing for better opportunities elsewhere. Even Iranian President Masoud Pezeshkian has claimed that up to 80 percent of students are contemplating emigration.
In an interview for this article, one young Iranian architect described his decision to stay as a “professional choice.” Architects in Iran can still pursue ambitious projects. For instance, Hooba Design Group has announced plans for a futuristic and eco-friendly residential complex in Kelarabad with a design guided by “regional architecture and local environmental laws.” Composed of stacked volumes of villas, each with their own glass facades and airy interiors, the renderings show a bold vision. Projects like this are encouraging Iranian architects to match the ambition of architects in Europe or the United States, where many had studied or worked before returning to Iran.
The homegrown team behind the Hooba project, like others, speaks to a sentiment articulated by the late Iranian architect, Ali Akbar Saremi. After having spent many years in the US, Saremi returned to Iran. When asked why he returned, he stated, “when I finished university and got my doctorate, there was no reason for me to stay there anymore. We wanted to return and develop our country… After all, our homeland is here and there was no reason to stay there.” His advice to rising architects was to “try to understand what is going on in the world,” as “we are the architects of a social class and we must understand the ins and outs of our society as well as other societies.” Such ideas have proven influential, with many Iranian architects thinking actively about their capacity to use architecture to shape social relations.
The most ambitious architects are further encouraged by opportunities for domestic recognition in the field. Memar Magazine, founded in 1988, is a bimonthly Persian publication on architecture and urban design. The prestigious Memar Award was initiated by the magazine in 2001 and strives to recognise the most prominent Iranian architects and their projects. The prize promotes a tangible sense of prestige, motivation, and visibility for architects in Iran to establish themselves both domestically and internationally, “paving the way for them to attract more clients who seek progressive designs for their projects.” Putting young designers in the spotlight in this way is a critical aspect of their pursuit of larger projects, drawing in capital to this specific industry.
Iranian architecture has also earned international accolades. The Jahad Metro Plaza, for one, was recognised by the RIBA International Awards for Excellence, as well as the Dezeen Awards. Architect Alireza Taghaboni, upon winning the Royal Academy Dorfman Award, explained how he aimed for his architecture “to have a productive purpose in a country where the context is political,” representing concerns with domestic issues in an international context.
Alongside politics, Iranian architects must also consider the state of the economy. Notable architect Farhad Ahmadi has stated that “if architecture wants to flourish in a society, the culture, knowledge, management, and economy of that country must also flourish.” It may be surprising, therefore, that a country facing significant economic challenges is home to a burgeoning architecture scene. But wealthy Iranians consider real estate to be a safe investment, and thus the field is supported by a steady stream of private commissions—even as sanctions and other economic headwinds continue to affect the construction sector. Hossein Hamdieh, an architectural researcher, noted in an interview that ‘‘avant-garde designs are often created for moneyed minorities who have both the appetite and the means to invest in such lavish, costly projects.”
On the other hand, Iranian architects have long developed projects with specific social objectives, such as improving the welfare of ordinary people or addressing environmental issues. These projects are often delivered in partnership with civil society organisations. For instance, FEA Studio, on the behalf of the NGO Noor-e Mobin, designed an intricate network of classrooms in the desert, near Bastaam, Iran. Opened in 2014, the G2 Primary School, as it is called, is designed in ways that allow children to play freely, featuring open air rooms with balcony-style railings to maintain their safety. FEA Studio commented that “it's a complex in which the children can grow and taste life,” serving the pedagogical goals of the school.
In another social project, ZAV Architects fit adjustable outdoor curtains to the balconies of an girls orphanage in Khansar, Iran. The Habitat for Orphan Girls is a residential centre aiming to protect young women, ages seven to 16, supporting them to flourish in adverse life circumstances. This particular project drew attention in the context of the anti-hijab movement in Iran. The architects aimed to allow the girls a comfortable and protected outdoor space where they can sit without a headscarf or hair covering, but used a striking yellow color to make these liminal spaces visible.
ZAV Architects’ founder, Mohamadreza Ghodousi told Dezeen that the building has the aesthetic appeal of interacting colourfully with the rest of the city, while also reminding its inhabitants that the “hijab is dynamic and you may have the right to wear it or not.” The project won the Memar Award in 2020.
The current sentiment among Iranian architects may be best summarized by one of the best, Leila Araghian. Araghian won the prestigious Aga Khan Prize for her 270-metre long bridge, Pol-e Tabiat, which connects Taleghani Park and Ab-o-Atash Park in northern Tehran. When asked what she finds exciting about contemporary architecture and design, she responded: “the possibility to affect the environment which can affect the human experience of the space seems fascinating to me. It makes me feel powerful.” It is precisely this outlook that promotes architecture as a tool for social renewal, transforming quotidian spaces for Iranians to feel a sense of liberation, agency, and connectedness.
Architecture in Iran today is more than just an artistic or functional endeavor; it is a medium for expression, resistance, and societal transformation. As architects navigate the challenges of working within an increasingly restrictive political environment, they continue to create structures that serve as both aesthetic marvels and meaningful social statements.
Whether through luxurious glass facades symbolising a desire for transparency, or community-driven projects that foster inclusivity and interaction, contemporary Iranian architecture reflects the country’s shifting landscape. At its core, this architectural movement challenges perceptions of Iran, both domestically and internationally, proving that even in times of hardship, creativity and innovation can flourish. Architects in Iran are shaping more than just skylines—they are reimagining and rebuilding the very structures of public and private life.
Photos: Mohammad Hassan Ettefagh, Soroush Majidi, ZAV Architects
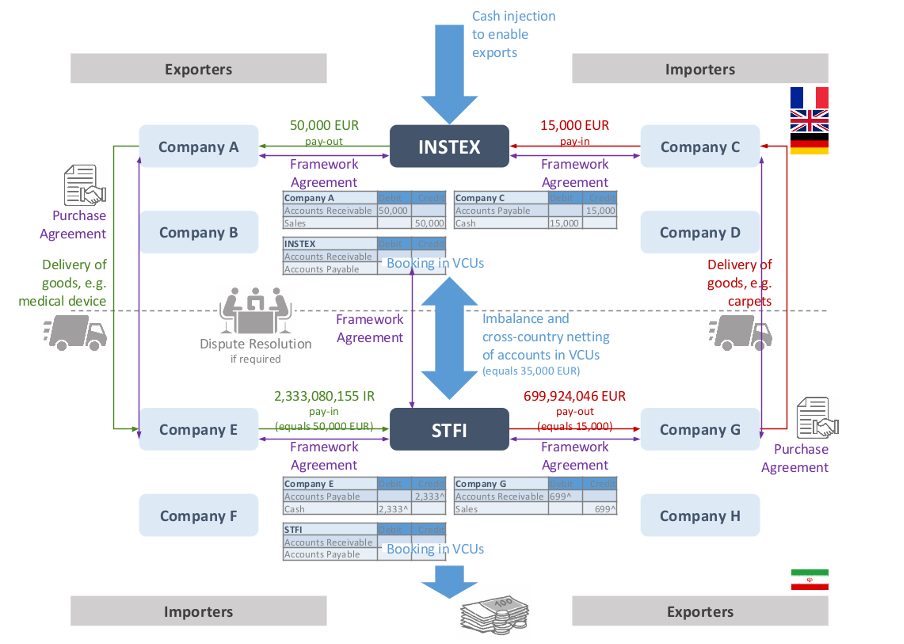
New Agreement Boosts Prospects for Connected Grids in the Gulf
A new agreement to finally connect Iraq to the Gulf Cooperation Council Interconnection Authority marks a significant step toward greater energy integration in the region.
The October 9 agreement to finally connect Iraq to the Gulf Cooperation Council Interconnection Authority (GCCIA) marks a significant step toward greater energy integration in the region. Originally established to link the power grids of the six GCC states—Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE—the GCCIA has been gradually expanding its reach. Iraq’s inclusion in this regional grid highlights the growing importance of cross-border energy cooperation to address the rising electricity demands in the Gulf. Iraq’s existing energy ties with Iran, however, suggest that the region could be on the verge of an even more ambitious project: a Gulf-wide power grid that includes all eight Gulf states.
Energy demand in the Gulf has surged over the years, driven by rapid population growth, industrialization, and the region’s heavy reliance on energy-intensive processes such as water desalination. Between 2010 and 2023, the Gulf's population grew from 153 million to 194 million, with projections indicating it could exceed 300 million by 2050. This population boom has placed immense pressure on power generation systems, which remain dominated by fossil fuels. In 2022, electricity demand alone accounted for about 15% of the total energy consumed in the region, with per capita electricity consumption growing by 74% between 2000 and 2022. This rise in demand is largely the result of increased industrial and commercial activity, infrastructure development, and economic growth, all of which require significant amounts of electricity.
Moreover, most regions surrounding the Gulf experience extremely high temperatures during the summer months, often reaching 50°C. As a result, space cooling has become essential, further driving up electricity consumption. The scarcity of freshwater in the region also leads to heavy dependence on desalination, which is a highly energy-intensive process. Reverse osmosis, one of the commonly used desalination technologies, is particularly reliant on electricity for mass production. Additionally, Gulf governments have historically subsidized electricity, making it relatively cheap for consumers. While this has helped meet public demand, it has also encouraged inefficient consumption patterns.
As of 2023, the Gulf’s combined installed power capacity stood at 272 gigawatts, with 70.4% of electricity generated from natural gas, 25% from oil products, 2.2% from nuclear, 2.2% from renewables (hydro, solar, and wind), and 0.2% from coal. The residential and commercial sectors are the largest consumers of electricity in the Gulf, accounting for 40% and 30%, respectively. In contrast, the industrial and agriculture sectors make up 22% and 6%. In 2022, the total carbon emissions from electricity generation in the Gulf amounted to about 700 million tons, representing 38% of the region’s total energy-related carbon emissions.
Cross-border electricity trade has also become an important feature of the Gulf’s energy landscape to meet rising demand. Between 2016 and 2022, the accumulated electricity trade in the region amounted to 126.5 terawatt-hours (TWh). Notably, about 55% of this trade involved Iran, which exports electricity mainly to Iraq while importing from countries such as Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Turkmenistan. Iraq accounted for 40% of the region’s electricity trade, all of which was imported from Iran. The GCC countries accounted for the remaining 5%, exporting and importing electricity among themselves through the GCCIA grid.
Iraq, in particular, has struggled with chronic electricity shortages. Despite an installed generation capacity of around 29.4 GW, inefficiencies and under-maintenance have reduced Iraq’s available capacity to just 15.7 GW. In 2022, peak electricity demand reached 30.5 GW, nearly double the available capacity, leading to regular power outages. Iraq has long relied on electricity and natural gas imports from Iran to help meet its energy needs. In 2022, Iran exported 3.5 TWh of electricity to Iraq through four transmission lines, and the two countries signed a five-year agreement in 2023 to import 50 million cubic meters of Iranian gas per day. These imports have been especially crucial during the summer months when electricity demand peaks.
However, Iraq’s reliance on Iranian energy is complicated by US sanctions on Iran. Since the US withdrew from the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) in 2018, Iraq has received waivers to continue importing Iranian electricity and gas. Yet, delayed payments and mounting debt—estimated at $11 billion—pose significant challenges. Iraq spends about $4 billion annually on Iranian energy, but US sanctions have delayed the country’s ability to make timely payments, leading to substantial debt accumulation. To settle this debt, Iraq proposed an oil-for-gas barter deal in 2023, allowing it to repay Iran through crude oil. However, opposition from the US Congress and ongoing conflicts in the Middle East continue to hinder the smooth functioning of Iraq-Iran energy cooperation.
Iran itself faces significant domestic energy challenges, including infrastructure problems and environmental factors such as droughts that have reduced its hydroelectric output. In 2021, Iran faced a 12 GW gap between peak summer electricity demand and supply. These domestic issues highlight the potential benefits of integrating Iran into the broader GCCIA grid, which could help stabilize Iran’s power system while benefiting the region as a whole. Iran’s vast land area and renewable energy potential—particularly in solar and wind—could complement the Gulf’s energy needs. By connecting Iran to the GCC grid, the region could also better manage electricity demand across different time zones, as argued by Robin Mills, leveraging the 1.5-hour time difference between eastern Iran and western Saudi Arabia to extend the availability of solar power during peak hours.
The potential for a Gulf-wide energy grid that includes Iran, Iraq, and the six GCC states presents significant opportunities for enhancing energy security, sharing resources, and balancing electricity supply and demand across the region. However, significant challenges remain.
Expanding the GCCIA grid to include Iran would require substantial investment in infrastructure, including new transmission lines and modern grid management systems. Iran’s aging power infrastructure would need to be upgraded to ensure reliable connectivity with the Gulf states. Additionally, coordinating electricity markets and pricing across such a diverse group of countries would require careful negotiation and planning. Geopolitical tensions as well as US sanctions, pose other major obstacles to integrating Iran into the GCCIA grid.
Despite these challenges, a Gulf-wide grid could foster greater political and economic cooperation. Energy interdependence could reduce regional tensions and encourage collaboration on other critical issues, such as water security and climate change adaptation. The Gulf is particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, including extreme heat, water scarcity, and rising sea levels, all of which could destabilize power grids. Multilateral cooperation on energy could play a key role in mitigating these risks in the Gulf.
The agreement to connect Iraq to the GCCIA represents a turning point in the Gulf’s energy landscape, opening the door to broader regional cooperation. With regional diplomacy expanding between Iran and the Arab states of the Gulf, the possibility of integrating Iran into a Gulf-wide electricity grid becomes an increasingly tantalizing prospect.
Photo: GCCIA
Can Abbas Araghchi Reshape Iran's Foreign Policy?
Iran’s new foreign minister has an opportunity to reshape the country’s foreign policy, cutting a creative path through the rigid confines of the political landscape.
On August 21, Iranian lawmakers confirmed veteran diplomat Abbas Araghchi as the country’s new foreign minister. Araghchi secured the support of 247 out of 288 MPs in Iran’s parliament, the Majles. Despite the vote total, Araghchi’s nomination was fiercely contested by hardliners. His confirmation hearing reflected the ongoing struggle between pragmatism and hardline revolutionary ideals that continue to shape the country’s foreign policy, and previewed many pitfalls he will face as foreign minister.
To secure his confirmation, Araghchi, like all of President Masoud Pezeshkian’s cabinet nominees, reaffirmed his unwavering loyalty to revolutionary ideals of the Islamic Republic and the Supreme Leader’s directives. Araghchi was addressing a legislature dominated by hardliners. During the parliamentary elections in March, the Guardian Council, a vetting body, had disqualified many moderate candidates. Voters responded by boycotting the elections and hardliners solidified their hold on the legislature.
While many of Pezeshkian’s nominees faced resistance, Araghchi’s confirmation as foreign minister was especially fraught. The confirmation hearings also took place while Iranian officials await the outcome of the Gaza ceasefire negotiations and continue to warn they will hit back at Israel for the assassination of Hamas political leader Ismail Haniyeh in Tehran on July 30. In Iran’s current political climate, loyalty to the revolution is often measured by one’s stance on foreign policy issues, particularly regarding the U.S., Israel, and Iran’s support for “resistance front” groups such as Hezbollah and Hamas. Any deviation from the hardline position on these issues is characterized as betrayal.
Iran’s Supreme Leader, Ali Khamanei, sets the strategic framework, redlines, and priorities for foreign policy, as underscored during his endorsement of Masoud Pezeshkian’s election on July 28. While the foreign minister and president must operate within these parameters, they still hold a vote in the Supreme National Security Council and can use public statements to put pressure on unelected bodies in Iran. Additionally, their personal ties to other national security figures, such as senior leaders of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), can enable them to influence policy.
Despite these means, the outgoing administration did not seek to actively shape Iran’s foreign policy. Neither President Ebrahim Raisi nor Foreign Minister Hossein Amir-Abdollahian, who were both killed in a helicopter accident in May, sought to advance a foreign policy that conflicted with the Supreme Leader’s redlines, the IRGC’s influence, or the parliament’s lawmaking. By contrast, the Rouhani administration, during which Araghchi was deputy foreign minister, publicly clashed with other power centers. This dynamic explains why Araghchi, like other nominees who served under Rouhani, drew sharp criticism from staunch hardliners.
Critics focused on Araghchi’s past as Iran’s lead nuclear negotiator, a role he held from 2013 to 2021. MPs like Mohammadreza Ahmadi Sangar and Mohammadreza Sabbaghian argued that the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), which Araghchi helped craft, was flawed from the start—a misguided deal that left Iran vulnerable to the whims of President Donald Trump, who withdrew from the agreement in 2018. Amirhossein Sabeti, a protégé of Saeid Jalili, who lost the presidential election to Pezeshkian, was perhaps Araghchi’s most vocal opponent. Sabeti argued that in the last months of the Rouhani administration, Araghchi was seeking a new nuclear deal that went beyond Khamanei’s redlines and would have effectively dismantled the resistance front. He also criticized the loss of nuclear capabilities that were key concessions of the JCPOA, including the decommissioning of the Arak reactor.
Iranian legislators have been seeking a greater role in defining Iran’s foreign policy. They want the kind of influence wielded by the U.S. Congress over international negotiations. In 2020, the Majles passed the Strategic Action Law, which effectively bars attempts to revive the JCPOA in its original form. The law, which was pushed by hardliners and endorsed by Khamenei, is as a double-edged sword—it provides leverage but also limits the flexibility needed to strike a deal that would relieve Iran’s economic woes.
For Araghchi, the JCPOA represented a calculated risk that preserved Iran’s position on the global stage, even as the Trump administration tried—and failed—to bury the deal at the United Nations Security Council. It is a legacy he has defended. During his hearing, Araghchi pointed out that the Raisi administration undertook its own nuclear negotiations. Even so, he indicated that he will take a fresh approach to any new talks and “strive to get the best agreement” in light of the Strategic Action Law. During his speech, he vowed to prioritize sanctions neutralization, a priority set forth by the Supreme Leader. But he also highlighted the necessity of lifting sanctions.
Araghchi understands that solving the nuclear issue is the key to addressing many of Iran’s economic challenges. The Pezeshkian administration aims to implement the ambitious 7th Development Plan, which targets an 8 percent annual growth rate—a goal that seems far-fetched given Iran’s economic isolation under sanctions. Iran needs around $60 billion in annual foreign direct investment. According to Hadi Ghavami, an MP who spoke in favor of Araghchi’s nomination, the country currently receives one-thirtieth of that amount.
During his confirmation hearing, Araghchi emphasized that while relations with the U.S. will continue to be defined by antagonism, his goal is to manage the rivalry and avoid escalation. This is part of the “heroic flexibility” needed to return back to the negotiating table. He also called upon Europe to enhance its ties with Tehran and to “return back to the list of areas of priorities for Iran.” The relationship with Europe remains fraught, clouded by the fallout from the JCPOA, the Woman, Life, Freedom protests, and Iran’s support for Russia in its war on Ukraine. Yet Araghchi emphasized that constructive global engagement is essential for any vision for development and managed to get hardliners to vote for him despite this vision.
Iranian officials have heavily invested in the country’s “Eastward turn” in recent years. The push for closer alignments with Russia and China began during the Rouhani administration but reached new heights under Raisi. But the strategy has not paid off. While Iran’s security relationship with Moscow is deeper than ever before, it has also become a liability, isolating Iran further from the international community. In a similar vein, China’s role as a key economic partner for Iran cannot be understated. Yet, there’s growing concern in Tehran that the relationship has become too one-sided, especially as Iran’s neighbors enjoy economic rewards from their trade with China.
At the same time, Tehran has recognized the opportunities presented by a shifting global landscape. Iran is looking to expand its influence into the Global South—Latin America, Africa, and East Asia. Through this understanding, multilateralism is a key factor in Iran’s core foreign policy strategy, reflected in the increasing involvement in platforms like BRICS, the Shanghai Cooperation Organization, and the Eurasian Economic Union. For Tehran, these alliances are more than symbolic; they are part of a broader effort to counterbalance sanctions pressure while positioning Iran as a significant player in a multipolar world. Pezeshkian has been invited to attend the upcoming BRICS summit in Russia in October, soon after he participates at the UN General Assembly in New York for the first time in September.
To secure the trust of the hardliners, Araghchi declared that “resistance diplomacy” is at “the foundation of Iran's foreign policy approach.” In this view, supporting groups like Hezbollah and Hamas is not just policy; it is a core principle of the revolution. Araghchi’s challenge is to convince the international community that Iran’s continued support for the resistance front is not an inherent threat to regional or global security. This is a difficult task when considering the fragility of the growing rapprochement and diplomatic engagements between Iran and the Arab states. There is considerable skepticism amongst Iran’s southern neighbors about the trajectory of the country’s foreign policy and whether deescalation can be sustained.
Ultimately, Araghchi will need to strike a balance when reshaping Iran’s foreign policy. He must find a way to pursue pragmatic diplomacy in a way that coheres with the ideas of resistance that hold sway over Iran’s hardline politicians. A cautionary tale can be seen in the legacy of Foreign Minister Javad Zarif, under whom Araghchi served as deputy foreign minister. Despite securing major concessions for Iran in various high-stakes negotiations, he failed to penetrate the conservative decision-making circles that ultimately dictate Iran’s broader foreign policy.
Araghchi may have more success. MPs appear encouraged by Pezeshkian’s effort to form a “unity cabinet” and seem to appreciate Araghchi’s closer alignment to key power centers. Iran’s new foreign minister has an opportunity to reshape the country’s foreign policy, cutting a creative path through the rigid confines of the political landscape. Whether he succeeds will depend on his ability to recast pragmatism as a tool of resistance.
Photo: IRNA
With Diverse Tactics, Women's Rights Activists Shaped Iran's Elections
Even if most women voters did not participate in the election, they still had a significant impact on its outcome
Although there are no official statistics on the number of women who participated in the fourteenth presidential election in Iran, evidence suggests that participation was limited. Mardomak, a research firm, reviewed a random sample of over 8,000 Iranian twitter users one week before the election. Of this sample, just 18 percent were women who supported Pezeshkian. Double that proportion supported one of the two hardline candidates, Saeed Jalili and Mohammad Bagher Ghalibaf, while 39 percent intended to abstain from the election.
But even if most women voters did not participate in the election, they still had a significant impact on its outcome. In a recent interview with the reformist newspaper Etemad, Shirin Ahmadnia, a sociology professor at Allameh Tabataba’i University, underscored the ways in which women have transformed the political arena through new forms of activism, including election boycotts.
For years, the Iranian women’s movement had adopted a “pressure from below, bargaining from above” approach to activism, aiming to bring about reform through a combination of tactics. But political elites were unswayed by the social pressure and unwilling to engage in good-faith negotiations—the situation of women remained largely the same, whether a moderate or fundamentalist was president. The Women, Life, Freedom movement, which emerged after the death of Mahsa (Jina) Amini, brought a new urgency to the fight for gender equality. Iranian women were no longer mobilizing to with the goal of reform. They wanted fundamental political change.
The death of Ebrahim Raisi in a helicopter accident led to new elections. Surprisingly, the Guardian Council, a vetting body, approved Pezeshkian to run. Faced with an unexpected election and a surprising candidate, some women activists did choose to vote, casting their ballots for Pezeshkian, who was backed by reformists and moderates. My conversations with nine women’s rights activists in Iran revealed complex feelings about the election and the best tactics to improve the status of women in Iranian society. Their names have been changed for their own safety.
Leila, an activist and writer, did not vote in either round of the election, but she deliberated voting in the second round. “I have not participated in elections since 2021. I asked myself: Should women participate in the elections when the presidential candidates promise nothing about women’s rights? As a woman, why should I participate in the elections of a state that does not show flexibility for women’s rights?”
Leila understood why some women may have opted to vote when Pezeshkian made it to the second round. “I think some of those who had not voted in the first round participated in the second round because [Jalili] represented religious fundamentalism, which worried me too. But in the end, I decided not to vote because I believed Pezeshkian’s chances of winning were high.”
Historically, women’s rights activists have been considered part of the reformist’s base. But a perceived neglect of women’s demands has led the reformists to lose much of this support. Maryam, a journalist who focuses on women’s issues has volunteered for reformist campaigns in the past. But she did not vote for Pezeshkian. She referred to a feeling of disappointment as candidates failed to make good on their promises. “I did not vote because I have no hope. My friends and I feel disillusioned with the reformists, with politics, and with elections. The president does not play a pivotal role in this dictatorial system.”
Many women experience double discrimination due to their ethnicity. Sahar, an activist from the Iranian province of Kurdistan, viewed abstention as a form of civil resistance. “I did not vote because civil laws, family rights, and political rights discriminate against me due to my gender,” she explained. “Legal reform has stalled for years. Moreover, my ethnicity, language, and identity still lack representation in political discussions.”
Sahar criticized Pezeshkian’s stance on women, adding “According to Pezeshkian, women’s social presence and gender justice are intertwined with their role within the family. He believes a woman’s identity should be defined solely within the family institution. In essence, women are denied individual freedoms and citizenship rights beyond household duties. His traditional thinking fails to recognize each woman’s independent identity.”
While many Iranian women grew disillusioned in the aftermath of the Women, Life, Freedom protests, for others, the turning point came earlier. For Haleh, who was jailed for her activism against the compulsory hijab law, this moment came after the downing of Ukraine International Airlines Flight PS752, which was hit by Iranian anti-aircraft missiles in January 2020. Explaining her decision to boycott the election, Haleh pointed to the failure of the government to create accountability.
“The main reason for me, even before the candidates were announced and before knowing whether we would have a reformist candidate or not, was that after the plane incident, I became disillusioned with the reforms,” Haleh explained. I was convinced that the path we had followed all these years would no longer work. In the past, I had hope and believed that voting for the reformists would lead us down the right path. But now, I ask myself, what difference does it make whether Jalili or Pezeshkian is president?”
While few women’s rights activists believe that Pezeshkian’s victory will lead to fundamental change, particularly on women’s issues, some believe that having a reform-minded president will make a difference. Many women’s rights activists saw voting for Pezeshkian as a chance to address economic hardships, revitalize social movements, and create greater space for women to voice their demands. Many women’s rights activists are struggling to make a living, which makes it difficult for them to sustain their activism.
According to Soudabeh, an activist and social worker, Pezeshkian’s promise to put technocrats back in charge of policy earned him the vote of some women. “They believed that Pezeshkian could address the deterioration of Iran’s economy by appointing people who are more knowledgeable and moderate to key positions. Iran’s situation is like a person with an incurable disease, and the Pezeshkian’s presidency might help slow or reverse the country’s deterioration.”
Some women’s rights activists working in governmental organizations or managing NGOs expressed a similar hope for the Pezeshkian administration. Shahla, an employee of a governmental organization, contrasted the Rouhani and Raisi governments. “During the Rouhani administration, despite its weaknesses, some women activists held management positions. With the fundamentalist representatives now in parliament, we cannot expect fundamental changes, but we are optimistic about social openings for women under Pezeshkian. Positive changes have already begun in our organization, indicating that while the president may not be able change the structure of the system, he can still influence social policies. I believe the state has acknowledged public dissatisfaction and is considering implementing changes, however small.’’
Despite Iran’s structural discrimination against women, some women’s rights activists still believe that they must not abandon the political arena. They seek improvements, however small, such as creating spaces to express their demands. Shadi, who runs an NGO for women, described the risks when fundamentalists gain power. “Most of us with NGOs working on women’s rights encouraged others to vote despite facing punishment for our activism. We endured the suffocating atmosphere of the Raisi era. Now, a small hope has emerged. Since Pezeshkian has been elected, some people in the governmental organizations we deal with have retreated from their fundamentalist stances.”
Shadi challenged the notion that activists should welcome the further deterioration of conditions in Iran. “Some have criticized me for founding an NGO, believing that increasing social problems could lead to the [Islamic Republic’s] downfall. In these years, so many women have been killed, yet nothing has happened to the state. These expectations are abstract. We must protect women and create spaces where diverse voices are heard,” she insisted. “We must not allow fundamentalists to take power in all three branches of government.”
Reyhaneh, an activist and law student, voted for Pezeshkian in the first round of the election. “I voted in the first round because I believe that the social movements need revitalization, and Pezeshkian’s presidency offers a greater likelihood of this compared to Jalili. Additionally, my decision was grounded in a pragmatic view of potential changes in the country.” Reyhaneh hoped for “less fear on the streets, less suppression of university students, and fewer professors dismissed.”
But she abstained in the second round. “In the second round, I paid closer attention to the debates, and the inconsistency of Pezeshkian’s statements about the economy dissuaded me from voting. For instance, he once emphasized that we should not allow people to experience poverty; yet in another context, he advocated for minimal government intervention.’’
Reyhaneh has low expectations as Pezeshkian prepares for his inauguration. “I don’t anticipate a reversal in policies regarding hijab, which concerns many of us. There may be some changes in the distribution of positions held by women, and more educated women may enter the government roles, but the glass ceiling will likely remain intact.’’
Saba, a sociologist who supported Pezeshkian, understands why many of her fellow activists refused to vote. She says Iranian women are engaging in “intentional neglect.” These women are no longer abstaining from voting to express anger towards Iran’s political elite. Instead, they are indifferent. “Women are signaling to the state, ‘We want nothing to do with you. We are forging our own paths, building our own businesses to maintain independence, crafting our own narratives, and creating separate media spaces on social platforms. Every day, we distance ourselves further from you,’” Saba explained.
In a campaign statement addressing “the main demands of today’s women,” Pezeshkian acknowledged that “today’s women do not want someone other than themselves to decide their marriage, education, career, clothing, and lifestyle.” Pezeshkian was the only candidate to issue such a statement, which declared that “the expansion and realization of gender justice will not only improve the condition of women but also to the revival of life in Iran.’’ He promised to “respect [women’s] choices” and to “provide a platform” for Iranian women “to become the best versions of themselves.”
Pezeshkian will begin his term without a mandate from Iranian women, but it is still in his interest to fulfill his promises to them. Should he fail to do so, Iranian women will boldly challenge him, as they have challenged his predecessors.
Photo: IRNA
Iran's Presidential Election Combines Low Turnout with High Stakes
Iran’s two presidential candidates have presented two diverging visions for the future of the Islamic Republic at a time when most Iranians have come to question the fundamental tenets of their political system.
The second round of Iran’s snap presidential election marks a critical moment for the country. On July 5, voters will decide between former deputy head of parliament Masoud Pezeshkian and ex-nuclear negotiator Saeed Jalili. While both candidates will struggle to restore power and prestige to the office of the president, the outcome of the election will be highly consequential for Iran, especially as the succession of Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei looms. Pezeshkian and Jalili have presented two diverging visions for the future of the Islamic Republic at a time when most Iranians have come to question the fundamental tenets of their political system.
The political divisions in Iran now extend beyond the long-running rivalry between “Principalists” and “Reformists.” Cleavages exist within progressive and conservative groups and between those who believe in the continuation of the Islamic Republic and those seeking fundamental political change. The record-low turnout in the election’s first round—just 40 percent of eligible voters cast ballots—reflects how a focus on ideological policies has alienated the electorate. In 2021, 18 million people voted for Ebrahim Raisi, whose shock death in a helicopter accident triggered new elections. On June 28, the combined vote for Jalili and third-place contender Mohammad Bagher Ghalibaf, the leading conservative candidates, totaled less than 13 million.
Reformists have likewise struggled to mobilize voters. Progressive Iranians want action on a wide ranging of issues, including women’s rights, internet censorship, political freedoms, minority rights, foreign relations, jobs and wages, healthcare, climate change, and education. While Pezeshkian, who received 10.4 million votes in the first round, has acknowledged these demands, most progressive voters do not believe he can foster change, and have so far stayed away from the polls.
Moreover, many Iranians opted not to vote because of a widespread belief that the election is illegitimate, owing to perceived election engineering and vote tampering. Many influential political figures have boycotted the snap elections, labelling the process an “election circus.” The sham election that brought Raisi to power in 2021 underscored the regime’s commitment to its own dogma, sacrificing decades of legitimacy earned through elections that were not free, but were competitive.
Raisi was a weak president, presiding over a system in which the executive’s powers are curtailed. Unelected bodies and interests groups enjoy significant influence over government policy in Iran and the Supreme Leader sets the red lines. Voters are under no illusions about the limits of the Iranian president’s power. But within the bounds of Iran’s political system, the divergence in the domestic and foreign policies of different presidents are often stark.
During the debates earlier this week, Pezeshkian and Jalili showcased their contrasting visions. Jalili comes from a self-proclaimed shadow government. He has led from the shadows for eleven years since securing just 4.17 million votes in the 2013 presidential election, which was won by Hassan Rouhani. Jalili champions a future where Iran is detached from Western influence. He vehemently opposes any engagement with the United States and, to a lesser extent, European countries. As a member of the Supreme National Security Council, Jalili used his political power to stymie revival of the Iran nuclear deal. Many fear that, if elected, Jalili might withdraw from the Non-Proliferation Treaty, thrusting Iran back into a nuclear crisis.
On the domestic front, Jalili’s camp includes ultra-conservatives vying for strict Islamic governance, more censorship, and tighter hijab laws and social restrictions. Even though Jalili has positioned himself as a kind of status-quo candidate, poised to maintain the policies of the Raisi administration, he is a divisive figure even within conservative circles. Some Raisi and Ghalibaf allies have indicated that they will support Pezeshkian over Jalili.
That Pezeshkian appeals to some conservatives points to the challenge he faces in mobilizing disaffected voters. His background distinguishes him from recent presidential candidates. He is an accomplished cardiac surgeon with certificates from the United States and Switzerland and served as Mohammad Khatami’s health minister. Some voters have connected with his personal story. Pezeshkian lost his wife and son in a car crash in 1993. He has not remarried.
Pezeshkian has said his foreign policy will be based on “engagement with the world,” which includes “negotiations for lifting sanctions.” Pezeshkian may be permitted to revive talks over the Iran nuclear deal—there is growing awareness among policymakers across Iran’s political specturm that sanctions relief is necessary for getting the economy back on track. However, he will face significant challenges in advancing his domestic policies. The parliament is dominated by hardliners, who will make it difficult for Pezeskhian to confirm his preferred ministers, which may include his outspoken campaign surrogates, former foreign minister Mohammad Javad Zarif and former communications minister Mohammad-Javad Azari Jahromi. Without an intervention from the Supreme Leader to encourage post-election unity, the political paralysis in Iran could prove even worse than in the final years of the Rouhani administration.
The specter of further political paralysis has no doubt deterred voters from believing in the viability of a Pezeshkian presidency. Boycotting the first round allowed the Iranian electorate to send a strong political signal that they will not allow their votes to legitimize a political system that is failing them.
But the stakes seem different now. A Pezeshkian victory appears a real possibility. If 10.4 million had not voted for Pezeshkian in the first round, it would have been reasonable for disaffected voters to completely boycott the election. But on the eve of the final round, voters may be thinking more tactically about the stakes of this election. A Pezeshkian presidency is a chance to hit the brakes at a time when Iran is accelerating towards a deeper political, economic, and social crisis. Whether Pezeshkian can turn the car around remains to be seen. But preventing Jalili from driving the country off a cliff might be reason enough to vote.
Photo: IRNA
Accelerating the Gulf's Energy Transition in the Wake of Russia's War
The Russian war against Ukraine has been both a gift and a curse for oil producers in the Persian Gulf. It has stoked oil demand, but also made clear the strategic necessity of the energy transition.
This article is part of a series exploring regional energy cooperation in the Gulf and is published in cooperation with Istituto Affari Internazionali.
The 2022 Russian war against Ukraine has been both a gift and a curse for oil producers in the Persian Gulf. In the short term, the war has created restraint for the development of renewables, contributed to the high oil demand, and in doing so demonstrated the need for more international investment in oil exploration and drilling. High oil prices and the resulting profits enabled the member states of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) to partially offset financial losses from previous years—and also benefitted the economies of these member states. However, the transition to a new model of global energy consumption has not been cancelled—it has only been delayed.
This conflict clearly demonstrated the economic risk of excessive dependence on hydrocarbon-based resources, and as a result the leading GCC countries began to develop clear action plans for speeding up the energy transition. For the Gulf’s traditional oil producers, this is a huge challenge: after the short hiatus forced by the war, the race to switch to renewable energy will restart and force the Gulf states to once again work against time to prepare the oil sector for the “post-oil” era.
In general, most GCC states base their current strategy on an understanding of two contradictory but coexisting trends in the global energy market—trends created by the war in Ukraine. The first relates to national security issues: individual countries may find it necessary to extend their hydrocarbon use. The second and conflicting trend is that some players may accelerate their transition to renewables for the same security considerations and to reduce their dependence on fluctuating hydrocarbon prices.
Economic Development and Political Considerations
If the GCC countries are to reduce their current economic dependence on hydrocarbon exports, they need to diversify on a large scale into renewable energies. Alongside this, there is a need to maximise income from oil exports—something which can be achieved by simultaneously reducing domestic consumption and increasing oil output. However, GCC members will need to avoid increasing the volume of CO2 emissions, as these damage the health of the population and cause environmental damage.
But the political considerations are tied to the rentier social contract model of the states in the GCC. This model is now becoming too costly; budgets are uncertain against a backdrop of fluctuating oil prices. The fourth energy transition—and related processes, such as decarbonisation, digitalisation, and the development of renewable and alternative energy sources—will enable Gulf states to generate additional sources of income to finance government subsidies and social programmes. The development of the renewables sector will additionally contribute to preserving the social contract, provided that its growth will also lead to the provision of new and high-paying jobs for the citizens in the public sector.
External Influences
Other countries are placing increasing pressure on GCC states to accelerate their energy transition—and to make the oil they export more environmentally friendly (a marketing requirement formulated by the global push for energy transition). To maintain the competitiveness of their oil in the global market, Gulf producers are forced to take steps to reduce the environmental harm that can be caused by the production and transportation of hydrocarbons. The active spread beyond the United States and the European Union (including in Asian countries, who have been the traditional sales market for the GCC countries) of what some term the “green agenda” further increases the importance of presenting hydrocarbon products as green and minimising the negative impact on the environment.
Moreover, GCC countries will inevitably be pressured by the international community to implement international climate agreements. In 2022, the Arab states took an active part in the COP 27 climate summit in Egypt, and again in 2023, when they held the COP 28 summit in the UAE. The latter was a major milestone: its final document not only summed up what the international community had done within the framework of the Paris Agreement, but also recognised the need to phase out energy derived from fossil fuels. In light of these developments, by early 2024, almost all GCC states had put forward their own net-zero emissions targets.
Circular Carbon Economy
It is important to note that the final COP 28 document calls for a gradual phase-out of the use of oil in energy systems but emphasises that this process should be carried out without prejudice to hydrocarbon producers. This duality fully meets the needs of the Persian Gulf countries. They are ready to provide consumers with hydrocarbons for as long as they are needed—for example, the European Union, which seeks greater independence from Russian supplies—and cooperate with the international community in preparing for a “post-oil” world. Under these circumstances, most GCC states now speak not only about the need to increase the proportion of energy generated by renewables, but also about the goal of creating a special form of the Gulf’s circular economy that could still be built on the base of the region’s hydrocarbon riches.
Thus, the so-called circular carbon economy concept promoted by Saudi Arabia does not reject the further development of oil and petrochemical industries of the Kingdom but implies the introduction of obligatory compensation measures for emissions through the active use of carbon capture technologies (CCUS). It also argues about the increased role of renewable energy sources in the production and transportation of hydrocarbons. Alongside these plans, the Gulf countries are also developing a strategy to become world-leading hydrogen producers.
Options for Cooperation
In Iran, deteriorating climatic conditions and attendant ecological problems are creating extra incentives for the government to increase its efforts to make the energy transition and restructure its economy. In a sense, the country started investigating ways to develop its own renewable sector long before the idea became popular among its neighbours. Possessing substantial hydro, wind, and solar energy-producing potential, Iran achieved substantial progress in developing these in 2000–2010. Unfortunately, any further progress was substantially slowed and in some areas even prevented by the sanctions placed on the country from 2010 onwards, although by 2022 Iran was still among the top five countries in the Middle East in terms of how much electricity is generated by renewables. Its experience in the renewables development field can still be of interest to other Gulf countries, and Tehran itself can learn a lot from the GCC member states about the use of CCUS technologies and renewables in the production and transportation of hydrocarbons.
The current situation might intensify levels of cooperation among the Gulf countries, and also between these countries and international partners. There is a good incentive to cooperate—between both the Gulf players within OPEC and those on the bilateral track—as the GCC economies and oil sectors will have a lot of challenges in common that they need to prepare for. Meanwhile, the Gulf states need to ensure a stable and long-term demand for Gulf hydrocarbons, which means regional players must invest more in Asian economies and attract Asian investments. Moreover, an important element of the Gulf countries’ economic strategies is now to attract and allocate in-house and international investments in both the traditional and renewable energy sectors.
Alongside other developments, the war in Ukraine has led to a clear intensification of European diplomacy in the Gulf and a revision of some past practices. Traditionally, European concerns about Gulf domestic policies limited the interaction between EU countries and GCC states in the energy field, but many of these concerns have been pushed aside. Instead, the European Union has demonstrated its readiness to help the GCC countries in their own transition to renewable energy sources, making it clear that it expects the Gulf to help the EU move away from its dependence on Russia’s oil and gas and ease the influence of geopolitical factors on oil prices.
Road Ahead
It is worth noting that the GCC countries do not intend to entirely replace the hydrocarbon sector with renewable energy production or to phase out oil usage or the development of petrochemicals. Instead, the Gulf states see the sustainable energy sector (as well as those industries accompanying the fourth energy transition) as a complement and addition to their hydrocarbon-based economies. The wealth they have accrued through hydrocarbons will allow them to accelerate diversification and make the “old” oil industry look eco-friendly. None of the Gulf states has abandoned plans to develop petrochemical production, seeing in it an opportunity to conveniently and easily diversify GCC economies and as a response to the question of what to do when oil is not in demand as feedstock for fuel production. As oil market analyst Tsvetana Paraskova puts it: “Renewable energy could replace more and more fossil fuels in power generation and transportation, but these are not the only industries using oil and gas. From medicines to cosmetics, clothing, and technology, the world will still need oil.” This is well understood in the Persian Gulf, and the various crises have shown that fluctuations in demand for hydrocarbons have not always depended on the demand for fuel.
In the medium and long term, adaptation to a new energy order would require Persian Gulf oil producers to restructure their economies and revise their social contracts to withstand a decline in demand and a reduction in prices for oil resources. They would need to rebuild their energy systems for a lower-carbon future while simultaneously ensuring the survival of their oil industries. Moreover, the Gulf states clearly understand the need to adapt to the growth of competition in traditional markets, particularly in Asia, and will need to consider multilateral cooperation to offset some challenges.
Looking into the future, the hydrocarbon production and petrochemical sectors will remain the backbone of the Gulf countries’ economic structure. The main motivations that shape the development plans in the region are twofold: to increase sources of income through diversification, including the development of hydrogen exports; and to ensure the profitability of the traditional oil sector for as long as possible. The likely success factors in this quest will be the reduction of the cost of producing both hydrocarbon-based and sustainable energy, the reduction of harmful emissions from traditional industries, and the maintenance of the necessary level of investment in both the oil sector and the new energy sources. As UAE Minister of Energy and Industry Suhail Mohammed Almazroui succinctly put it, “drop the cost, drop the carbon, maintain the investment.”
Photo: Dubai Protocol Department
The Case for Cooperation on the Energy Transition in the Gulf
Embracing shared objectives, drawing on collective strengths, and navigating challenges with a collaborative spirit will the Gulf region towards a future defined by sustainability, resilience, and mutual prosperity.
This article is part of a series exploring regional energy cooperation in the Gulf and is published in cooperation with Istituto Affari Internazionali.
Regional security and economic development among the Gulf states—Bahrain, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE)—can improve if cooperation is fostered in the energy, minerals, and water industries, by encouraging joint exploitation of resources, establishing neutral regional zones, and creating energy sources that are interconnected. The positive diplomatic environment of 2023, particularly after the rapprochement between Iran and Saudi Arabia after seven years, holds the key to unlocking a new era of cooperation in the region across the resource mix.
Fostering Renewable Energy Cooperation
The region’s geographic location means it receives some of the highest annual amounts of solar energy in the world—more than 2,100 kilowatt-hours (kWh)—and a wind speed that can reach about 10 meters per second (m/s). These natural clean energy resources could be exploited regionally and also exported beyond the region, benefitting the economy both directly and indirectly and encompassing many sectors of industry, including energy, manufacturing, and information technology.
The Gulf Cooperation Council Interconnection Authority (GCCIA) envisions establishing a robust interconnected power grid. This would leverage the region’s abundant solar and wind resources and further position the are to become a hub for producing and exporting clean energy. As of early 2024, part of the region is already interconnected through this grid—from Oman in the south through the UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, and Bahrain, and then to Kuwait in the north. In addition, Iraq recently signed an agreement with the GCCIA to join the grid. GCCIA has an ambitious plan to extend to Eurasia and East Africa. Iran is also part of this planned grid, as is Turkey. Such interconnection would give domestic power grids more reliability and stability in the face of increasing challenges, such as unexpected electric load rise, as well as blackouts due to natural disasters or equipment failures.
Envisioning a Gas Network
Expanding the gas sector across the Gulf is a potential solution to some of these problems. Doing so would pave the way for a joint gas pipeline network that could facilitate hydrogen transmission—which is key to achieving net zero carbon emissions. Several Gulf countries have either not fully developed their gas production sectors or have insufficient resources. Iraq, Kuwait, and the UAE are net gas importers, and in 2022 imported 50%, 40%, and 20% of their gas demand respectively (see chart below). For example, Iraq imports most of its gas from Iran, and the UAE sources much of its gas from Qatar through the Dolphin pipeline.
Kuwait is the only Gulf country to source a large percentage of its imported gas (46%) from non-Gulf regions, such as Africa, Europe, and North and South America. This sourcing of around 4 billion cubic meters of natural gas annually from faraway countries is deemed to be a lost economic opportunity for Gulf countries, including Iran and Qatar.
Expansion of the gas sector in the Gulf would play a key role in the region’s energy transition. Having a joint pipeline network capable of carrying hydrogen products could also pave the way for the region to become a world hub in the production and export of carbon-neutral (blue and green) hydrogen.
Gulf Minerals Powering the Future
The Gulf region’s mineral wealth, essential for energy transition, has come to the forefront. Recent discoveries of lithium, cobalt, nickel, copper, and other minerals mark a turning point in the global race to secure mineral supply chains. These minerals are essential components of renewable energy technologies and energy storage systems.
Recently, Iran announced the discovery of a huge lithium deposit—an estimated 8.5 million metric tonnes—on its territory. This makes the country the fifth lithium reserve resource holder after Bolivia, Argentina, Chile, and the United States. Moreover, Iran also revealed the discovery of additional vital minerals, among them manganese, nickel, and cobalt.
Saudi Arabia also recently announced the discovery of mineral reserves with an estimated market value of US $64 billion. Among the discovered minerals related to energy transition are copper, iron, and nickel. Oman, too, has announced an ongoing project to update its national geographical and geological minerals database with more discoveries of copper and iron reserves.
The envisioned regional collaboration would include joint investments in developing the infrastructure needed in the region for extraction, preliminary mineral processing, and export logistics. Joint efforts to invest in the management of mineral resources could position the Gulf as a key influencer in the global transition to clean energy. This could be pursued by establishing joint venture companies where investors include the Gulf states’ public and private sectors.
Working together, the Gulf states could pool resources, share costs, and achieve economies of scale. By doing so, the region would be able to collectively manage and mitigate risks associated with volatile commodity prices, environmental challenges, and geopolitical uncertainties. As a result, such collaborative ventures would contribute to political stability in the region. The Gulf countries would have broader access to markets and assert their role as key players in the energy transition agenda.
It is worth noting that Iran’s current economic sanctions may discourage other states from establishing joint ventures. However, these restrictions do not prevent discussion of joint strategies for making the most of the Gulf’s mineral reserves and developing regional value chains.
Developing Shared Fields
The collective strength of Gulf countries lies in their vast natural resources, accounting for approximately 48% and 40%, respectively, of the world’s proven oil and natural gas reserves. Shared oil and gas fields, as illustrated in the table below, are poised for active development, offering potential solutions to regional energy challenges.
In early 2022, Kuwait signed a memorandum of understanding with Saudi Arabia to develop the joint offshore Arash/Durra gas field in the partitioned neutral zone. However, Iran has objected to the agreement and demanded its share. Most likely the Arash/Durra field will not be exploited in the short term until an agreement is reached on the demarcation of maritime borders between Iran, Kuwait, and Saudi Arabia. However, joint exploitation of Arash/Durra could be achieved without compromising the territorial sovereignty of the three countries; Iran is already jointly exploiting oil and gas fields with neighboring Gulf states, including the South Pars/North Dome gas field with Qatar and the Esfandyar/Lulu oil field with Saudi Arabia. These joint models can provide lessons and open the door for pragmatic and logical negotiations to enable cooperation in exploiting other joint fields, including Arash/Durra.
Establishing a Regional Water Network
A region is labelled as water-scarce when the availability of natural renewable water (waterfalls, rivers, freshwater lakes, and aquifers) is below 1,000 cubic meters per person per year. This definition implies that all Gulf countries except Iran are under the natural water poverty line. Consequently, these countries depend on energy-intensive seawater desalination to meet their potable water demand. The power stations in these countries are mostly cogeneration systems that produce electricity and heat.
Addressing water scarcity is paramount for Gulf countries, especially those heavily reliant on desalination. Despite challenges including geopolitical tensions, a strategic imperative is to establish a regional water interconnection network. With this in mind, GCC leaders decided to carry out a water interconnection study in the year 2000. The proposed network would supply fresh water to all GCC states from desalination plants that would be built on the shores of certain states. Three desalination plants were proposed—to be built in Sohar, Oman; Al-Sila in the UAE; and Al-Khafji in Saudi Arabia. Unfortunately, there has been no tangible action on the project since 2013.
There is an urgent need for increased cooperation in the areas of seawater desalination, water treatment, water resource management, and water transmission across the Gulf region if its future is to be more sustainable. The latter of these in particular is a key survival strategy, and such a water network would make the region resilient to natural and changing environmental conditions challenges. The feasibility of a regional water grid should not therefore purely be based on financial profits—it also needs to consider the grave water scarcity challenges the region is poised to face in the years ahead.
Moving Towards Sustainable Horizons
While it may take time to achieve regional cooperation in energy, water, and environmental sustainability, diplomatic rapprochement between Iran and Saudi Arabia could pave the way for positive outcomes. Policies should focus on establishing interconnected regional infrastructures, including gas and water networks, and implementing a joint financing system to support balanced development across the Gulf region. It is essential to overcome political differences and address challenges through dialogue for these policies to succeed.
As we chart the course toward sustainable horizons in the Gulf, the call for cooperation echoes loudly. Embracing shared objectives, drawing on collective strengths, and navigating challenges with a collaborative spirit will propel the region towards a future defined by sustainability, resilience, and mutual prosperity.
Photo: Shams Power
Rising Electricity Demand Requires New Thinking on Gulf Grids
The complexity of Gulf power markets has significantly increased due to climate change, making it essential to pay more attention to how systems are planned and designed.
This article is part of a series exploring regional energy cooperation in the Gulf and is published in cooperation with Istituto Affari Internazionali.
The demand for power is rising in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region; the 2023 Electricity Market Report by the International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that this demand will grow at an annual rate of 2 percent in the 2023–25 period. Most of this growth is driven by Iraq, Iran and Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, notably Saudi Arabia, Oman, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE). For these countries, the same report expects electricity consumption to increase, on average, by 2–3 percent between 2022 and 2025. The main drivers of this are population growth, and specific uses such as cooling and water desalination.
The effects of climate change, such as a higher number days when maximum temperatures exceed 35 degrees Celsius, are driving demand upwards in the region. But measures to boost energy efficiency are also on the rise. A recent IEA study based on temperature projection models shows how these trends are particularly affecting the region. For example, Saudi Arabia has accelerated the roll-out of smart meters in the country while partially reviewing its electricity tariffs to support more rational consumption patterns. If these measures were maintained and widened throughout the region, the growth of demand for electricity would potentially be mitigated. The Emirate of Dubai currently has over two million smart meters installed. Oman also has a national smart meter programme overseen by the Authority of Public Services Regulation, which aims at installing 1.2 million smart meters by 2025, covering all of the country’s electricity consumers.
At the same time, oil and gas remain dominant in the MENA region, with natural gas playing a prominent role. During 2023–25, the IEA expects gas-fired power to generate the most electrical capacity. For instance, in 2024, the same IEA report predicts that two thirds of the 60 gigawatt (GW) capacity being added to the whole Middle East region are expected to come from natural gas, with the rest being split between nuclear and renewables. At the same time, these countries are seeing the effects of renewable energy sources being increasingly deployed, in particular solar photovoltaics (PV).
Between 2023 and 2028, the IEA predicts that the Gulf region is expected to increase its renewable power generation capacity by over 40 GW. This represents almost half of Saudi Arabia’s current power generation and is more than the total power generated by the UAE today. This growth is dominated by utility-scale solar PV. In addition, the report cited that hydrogen also represents around 13 percent of extra renewable power capacity, mainly enabled by government-backed incentives to stimulate hydrogen trade. Other factors supporting the growth of renewables for hydrogen include high levels of solar irradiation, land availability, and port infrastructure.
While this growth remains impressive, it could increase faster. Possible strategies to further accelerate growth might include encouraging more competition between utility providers, introducing domestic tariffs that reflect individual users’ costs, addressing contractual issues with existing fossil fuel providers, and better supporting power storage systems to be flexible.
Cross-border electricity trading can also improve the deployment of renewables. However, international connections in the Gulf today only represent a small proportion of each country’s electricity consumption. The six-member GCC Interconnection Authority, which has the remit to do this, was established in 2001, but as of 2024 has only been able to support 1.2 GW of capacity. The recent linking of Iraq to the network through Kuwait, and ongoing discussions about a Saudi–Iraqi connection, would strengthen the region’s interconnectedness in terms of power generation.
Of course, regional particularities need to be considered, for example consumption patterns related to climatic conditions. Innovative economic models are needed to address the need for system flexibility as a result of changes in peak demand between seasons, and between day and night. While leaders in the GCC are looking into the diversification of power supplies without compromising grid stability—whether through renewables or nuclear—leaders in Iran and Iraq face a growing mismatch between supply and demand.
For instance, in 2021, Iran had to face a 12 GW gap between peak summer demand and supply. Severe droughts limited hydropower in a country that generates 4.6 percent of its electricity from that source. Although there were also other factors at play, both domestic and external, the effects of climate change and limited diversification in the power generation sector cannot be discounted as factors limiting the overall resilience of the current system. Neighbouring Iraq also faced similar challenges, despite the domestic context being different. Nevertheless, both countries are investigating whether renewable power capacity can be developed faster. For example, Iran has set a 2025 target for 10 GW of renewables, while Iraq is looking into linking oil and gas investments with large-scale renewables projects. However, it is worth pointing out that reforms in the electricity market remain a key prerequisite to address the power sector crisis.
There can be no large-scale transformations in electricity markets without adequate reforms. In the Gulf, there remain vast opportunities related to tariffs and subsidies. While investments in renewables in the region have been enabled by the active involvement of governments (where land availability and permissions enable large-scale projects, such as in Oman and the UAE), tariff and subsidy reforms should remain a priority. Otherwise, current and future renewables projects will not be financially viable. Reforms such as these would also allow utility companies in the region to recoup their costs and allow for investments in the grid infrastructure. These investments would pave the way for further renewables to be developed and deployed, such as decentralised solar PV.
The dynamics surrounding power markets in the MENA region require addressing a series of priorities that sometimes come into conflict with each other. Governments are expected to provide secure, reliable, and affordable electricity to all. In a geographical area significantly affected by the effects of climate change, the need to mitigate these impacts is probably more pressing than in any other region. Climate change not only creates new patterns in demand, with a heightened need for cooling and desalination, but it also affects the resilience of the power system itself. Higher temperatures, droughts, higher sea levels, or flash floods can all significantly affect operations on the supply side and reduce output. This is not limited to conventional power generation (oil and gas); nuclear and solar PV units can also be affected.
In this challenging regional context, where priorities are continuously shifting, it remains important that the climate crisis increasingly plays a central role in how regional leaders think about their future energy systems. Climate change has significantly increased the complexity of power markets. It is essential to pay more attention to how systems are planned and designed, and how they must operate in the face of new demands.
Photo: Emirates Nuclear Energy Corporation
Iran's Instagram Crackdown is Jeopardising Women's Livelihoods
In recent years, Iranian women have accounted for a growing share of major Iranian accounts on Instagram, seizing economic opportunities that are unavailable in Iran’s offline economy. Today, that progress is at risk.
Iranian women have been striving to enhance their socioeconomic status, both online and offline. Statistics show that this is not an easy task: in 2023, the World Economic Forum ranked Iran 143rd out of 146 countries in its annual gender gap report. Iran also sits at 144th for economic participation and opportunity. Consequently, many women resort to informal employment in areas such as sales, homeworking, catering, and domestic work. Due to the informal nature of this kind of work, it is difficult to collect data on the number of women in such roles.
Although it has become increasingly difficult for Iranians—particularly women—to make a living, many micro-entrepreneurs have used Instagram to start businesses. Due to its relatively low entry barriers and easy access to potential customers, the platform had been ideal for this purpose. However, Iranian women are now encountering serious obstacles. A move by authorities to block Instagram and throttle internet speeds, as well as steep increases in internet package prices and arrests of prominent influencers, have all made it more difficult for women to seek economic opportunities online.
World Bank figures from 2021 show that approximately 79 percent of Iran’s population uses the internet. In February 2024, the Iranian Students’ News Agency (ISNA) reported that after Telegram, WhatsApp was the most popular platform, with about 47.7 million users. Instagram ranked third, with 47 million users. Of Iranian Instagram users, 46 percent are female—more than 21 million women.
For the last five years, Abolfazl Hajizadegan, a sociologist at the University of Tehran, has published an annual report on Iran's social media sphere. Hajizadegan’s most recent report clearly shows that, despite the shutdown of Instagram by the Islamic Republic (which occurred at the beginning of the Woman, Life, Freedom movement in Iran), women persist in their online presence.
In this piece, I have chosen to focus specifically on accounts from which influencers generate income. The accounts I discuss do not necessarily belong to the most famous people but to ones who have amassed a large number of followers and are engaged in online business.
The table above is drawn from Hajizadegan’s reports and shows that the share of women has increased among Iranian social media influencers. Among lifestyle-oriented accounts on Instagram, the proportion of women has risen from 58 percent in 2019 to 89 percent in 2023. One of the women who has experienced the highest growth in followers in recent years is Yegane Rezaee, a lifestyle blogger. With one million followers, she chronicles her daily life and earns an income through sponsored posts.
Women are strongly represented among fashion and beauty accounts and one of the influencers in this area is Farzaneh Mezon, who has 153,000 followers. Mezon advertises her products by showcasing various outfits in the photos she uploads. Perhaps because of her popularity, her online store was blocked in July 2023. She soon posted the following statement on Instagram: “Our website has been blocked by a court order. We have been asked to delete all photos that go against Islamic values and the proper hijab framework.” Farzaneh was able to continue her work after appealing to her followers, who wrote comments of solidarity under the post and vowed to support her in making the necessary changes to her website.
Iranian women also account for a growing share of Instagram accounts focused on educational content. The share of women-led accounts has risen from 14 percent in 2019 to 45 percent in 2023. Havin Hosseiny manages a page that focuses on empowering women by improving their life skills. Her bio states, “Our goal is to improve women’s mental health and help them increase their income.’’ With 739,000 followers, she explains gender equality to the audience on her page by publishing short animated videos with attractive content and simple language. She also founded the Havin School, which offers online courses for women that focus on issues such as personal relationships, career advancement, self-confidence, stress reduction, and financial awareness. In addition to providing free educational content, she earns money from other educational workshops.
In the comedy and entertainment field, the gap between women and men remains significant despite women’s share increasing from 6 percent in 2019 to 29 percent in 2023. Zeinab Musavi, known as Emperor Kuzco, creates short comic videos. With 645,000 followers, she is one of the most famous Iranian comedians online. To earn an income, she asks her followers to donate any amount they wish: “These videos I create and publish on this page are my job. And if you enjoy them, you can contribute through two links I have provided in my bio.’’
Men dominate the sports pages. However, pages such as the one run by Elnaz Rekabi, a competition climber with 653,000 followers, are among the most popular on Instagram. It is worth bearing in mind that the low number of women participating in this field likely reflects restrictions placed on female athletes. For instance, the Instagram page of Sogol Rahbar, a bodybuilder with 290,000 followers, was temporarily shut by the Law Enforcement Command of the Islamic Republic of Iran, known by its Persian acroynym, FARAJA. A post on Rahbar’s account carried this message: “Due to the publication of criminal content against public morals and decency, Faraja has blocked this page.’’ However, after deleting posts deemed to depict “improper hijab,’’ Sogol resumed her activities. She earns money through advertising, providing exercise and nutrition programmes, and conducting online classes.
According to Hajizadegan’s research, women do not run any popular religious pages. However, conservative values are represented in other spheres. For example, there are business pages run by conservative women, one of whom is Khadije Faghih, who teaches mat weaving and has 37,800 followers. In addition to publishing free educational content, she earns money by holding classes.
Because Iranian women are excluded from the formal economy, many have sought opportunities in the informal economy. The widespread use of social media platforms has allowed many creative and enterprising women to engage in online business. Instagram is one of the most widely used platforms in Iran, but the crackdowns following the Women, Life, Freedom movement, have created new obstacles for women seeking opportunities on the platform. Moves by authorities to pressure women to observe the “proper hijab’’ have economic consequences. Moreover, President Ebrahim Raisi has yet to fulfill an election promise to provide free internet to all people on low incomes. Instead, internet prices remain high, and the government filtering of platforms like Instagram means that people are forced to buy virtual private networks (VPNs). This has dramatically reduced internet access for economically disadvantaged women.
According to the Tehran-based Beta Research Center, more than two million Iranian businesses market products and services on Instagram, and less than one-fifth of these enterprises also sells their products offline. Importantly, 64 percent of these businesses are owned by women, who have been disproportionately impacted by the internet crackdowns. Rural women who relied on online businesses for their livelihoods have been especially affected—many have been forced to peddle their products on city streets.
In February, Iran’s National Center for Cyberspace officially prohibited the use of VPNs. At present, despite campaigns to repeal the new prohibition, the future of the Iranian internet is uncertain. In recent years, Iranian women have accounted for a growing share of major accounts on Instagram, seizing economic opportunities that are unavailable in Iran’s offline economy. Today, their livelihoods are in jeopardy.
Photo: Farzaneh Mezon
How Female Vendors in Tehran's Metro are Forced Underground
With both economic sanctions and government policies damaging women’s status, female vendors are fighting on domestic and foreign fronts to sustain their livelihoods.
“It is like working in a mine; you use subways for commuting, but we have to work underground for at least seven hours,” said Soudabeh, a young woman who works as a peddler in the Tehran Metro. To protect her anonymity, I have changed her name, along with those of all the women interviewed here.
The number of female vendors working in the subway is growing, but no official statistics record how many there are. They are an integral part of the daily life of Tehran Metro: circulating among passengers with bags containing cosmetics, socks, clothes, sandwiches, books, and more. Most female vendors work in the front and rear wagons of the trains, normally designated for women. Despite the efforts of municipal authorities and police to curb their activities, they persist in utilising the public transportation system as a workplace.
Women marginalised from Iran’s formal economy resort to making a living in the subway. Soudabeh is one of the thousands of female vendors. She is divorced and living with her mother. Peddling is only a secondary occupation for Soudabeh, who has been working since high school. She is a fitness trainer and works mornings in a gym, but her wages from that job are not sufficient to meet the household’s needs, so she must also work underground, in the metro.
Making ends meet requires Soudabeh to work even on holidays. She underscores the significance of financial independence for women: “A woman who has income can decide for herself. Women should have the capacity to tackle their challenges in society. If a woman who has a job gets divorced, she will not tell herself I burned all the bridges behind me and do not have a way to survive.”
In the past, children often took their parents’ place in a family business. Today, however, when all they may inherit is poverty, they follow their mothers into the metro to earn money.
Ala has not gone to university because she thinks it is futile for her future. Her mother’s twelve years of work in the subway became Ala’s path, too. Still, she considers working in the subway to be better than having an employer: “Working for yourself is better than working for other people. An employer might not provide me with a steady income. My friend’s employer did not pay her because his store did not sell for a month. Here, in the subway, you have your daily earnings.”
Flexible working hours and being your own boss are motives that many female vendors emphasise when asked why they do the job. Faced with patriarchal norms in society that expects women to do housework and take care of children, leading to a dearth of employment opportunities, they have little choice but to be self-employed. Mona sells bags and hats. She suffered from domestic violence and recently got divorced. Born in Mashhad, she has worked since she was twelve years old when she had to quit school because her family could not afford to keep her in education. She migrated to Tehran after her marriage. After several years working in a restaurant, Mona had to change her job and became a subway vendor: “I worked in a restaurant. I love socializing with people. When I worked there, my passion for the job was so intense that customers thought it was my restaurant. However, I had to quit my job due to my circumstances. Daily responsibilities such as picking up my daughter at school make flexible working hours in the subway a practical choice to me.”
Economic instability is one of their persistent concerns. Many have to go to the bazaar daily to acquire goods, and they face escalating prices influenced by the fluctuating value of the US dollar. Tara resides in Navab and has a bachelor’s degree in IT. She sells rhinestones and jewlery, purchasing some of her goods from the bazaar while others are hand-made. She expresses concern about escalating dollar prices: “I remember when the dollar suddenly surged to fifteen thousand tomans. I got so stressed that I failed all of the final exams. Why should I be worried about the dollar’s price?! If prices were stable, we would not endure this relentless pressure.”
Rising prices are a concern because vendors do not have much capital to stockpile goods. Indeed, the minimal initial outlay requirement is one of the reasons women choose this job. Tara, struggling to find an IT job in a company, took goods from her brother, also a vendor, to the subway to sell. “My mom works in people’s homes. I did not want to depend on her financially anymore. My mom is exhausted. I pondered how I would make money to assist her. So, I decided to work. Observing young women like myself work in the subway, I thought, ‘Why not me? Why do I not work?’ One day, I went to the metro but could not sell anything. I felt shy. But after four months, I could not bear the financial strain. I brought some of my brothers’ goods on the subway. A female vendor guided me. I told her, ‘I cannot advertise because I feel shy.’ She assured me she would teach me. We sold all the tops together, and its profits became my initial capital. After that, I brought chewing gum, and now I sell rhinestones.”
Sanctions contribute to an economic crisis that has exerted the greatest pressure on the lower classes. Forouzan resides with her family downstairs in her mother-in-law’s home in a disadvantaged district of Tehran. She sells scarves to make ends meet. The night before we spoke, she had learned she was pregnant. She was thinking about whether to keep her baby or have an abortion. Her husband works in a relative’s shop. His salary is insufficient, so both must work to cover their needs. Forouzan has a bachelor’s degree in economics and had worked in a bakery before vending on the subway. She observes the economic strain on the lower classes: “I think the elite become richer following shocks such as sanctions and surges in the dollar price. Their properties, homes, and cars become more valuable, but people like us become more and more vulnerable.”
One of the most formidable challenges female vendors face is daily confrontation with municipal agents and police officers. The officers try various tactics to expel the peddlers, such as confiscating vendors’ goods. Despite these challenges, the women continue their work, but they feel the pressure of such daily stresses. One female vendor wondered, “If they become successful in preventing us from working one day, what will happen to my family and me?”
To prevent the agents from confiscating their goods, women have developed ways to outwit them. In central stations like Khomeini, where there are greater numbers of officers, they do not get out of wagons. Some pretend they are passengers. Others employ strategies like concealing goods under a chador or in their bags.
Yalda and her husband both work in the subway. Yalda sells underwear. “I know which stations have more agents and avoid getting off there,” she explains.
The stories of these women show them grappling with patriarchal norms, state policies, and economic precarity. They also show the men in their lives worried about losing their bargaining power if their wives earn wages. Paradoxically, harsh financial circumstances often compel them to accept women’s economic role.
Yalda’s husband did not allow her to register at university. However, their financial problems meant she was able to convince him to allow her to work. Eventually, compelled to quit his job when they failed to pay his salary, he too stepped into the work Yalda had begun, and now they make a living together as peddlars.
The state expects women to perform traditional roles, to be good wives and mothers. Policies reinforce conventional gender roles, and the home is deemed the most appropriate sphere for women. Female vendors’ experiences in their daily confrontations with authorities make it clear that the Islamic Republic’s policies not only fail to create formal job opportunities for women, but they actively work to exclude women from their hard-won informal employment.
I conducted these interviews in Tehran’s metro in 2019 and 2020. I talked to 111 female vendors. I immersed myself in their world and observed them working, escaping, and trying to survive. I sat beside them when they were working on station platforms, accompanied them inside wagons, and witnessed their escape strategies from the police and how they navigated challenges to their survival. I have been honored to listen to their stories and document their resistance.
With both economic sanctions and government policies hurting their prospects, female vendors are fighting on both domestic and foreign fronts to sustain their livelihoods.
Photo: IRNA
In Iran, ‘Ordinary Women’ Lead an Extraordinary Movement
One year has passed since the tragic death of Mahsa (Jina) Amini in police custody and the start of the Woman, Life, Freedom movement, which has induced cultural transformations within society and families in Iran.
One year has passed since the tragic death of Mahsa (Jina) Amini in police custody, the event that ignited the Woman, Life, Freedom movement. This movement has provided a platform for acknowledging the enduring struggles of ordinary women in Iran, a battle that had been ongoing long before September 16, 2022. By “ordinary women,” I refer to individuals outside the elite and activist spectrum, adapting from sociologist Asef Bayat’s definition of “ordinary people” in his book Revolutionary Life. The struggles of ordinary women in Iran were often ignored or sidelined until last year. While I respect the efforts of all women’s rights activists dedicated to improving women’s rights in Iran, I believe the “Mahsa movement” stands on the shoulders of ordinary women, many of whom may not belong to the middle class or possess feminist knowledge, but who are undeniably fighting for the freedom to lead ordinary lives.
The Woman, Life, Freedom movement has induced cultural transformations within society and families in Iran. Many parents who previously advised their daughters to accept the mandatory hijab as a “minor issue” have now thrown their support behind their daughters’ quest for freedom of choice. The presence of women with uncovered hair has become more widely accepted. Women feel safer going out without the hijab. As one woman told me, “before the Woman, Life, Freedom movement, when I went out without hijab, I felt I was breaking social norms and that I was doing something weird in the eyes of society. But now I feel safe and know if somebody scolds me about the hijab, other people in the streets will come to protect me.’’ These cultural changes in the Iranian society are not limited to the hijab issue. The status of women within families has largely changed, and more women are gaining autonomy.
One of the most intriguing aspects of the Mahsa movement is the newfound overt support from men. Women have historically borne the brunt of struggles against a patriarchal society and state, but the Mahsa movement marks a turning point where men have joined in supporting women’s causes. Whether this support will extend to other women’s issues, such as unequal inheritance and divorce laws, remains to be seen.
The Woman, Life, Freedom movement has also significantly transformed the subjectivity of ordinary women. It has united women with shared experiences and pain, reminding them that they are not alone. While there have always been small support networks among women, this movement has elevated this solidarity to a national (and international) scale. In one instance, I saw a police officer who wanted to confiscate a vendor’s goods in the Tehran subway. Women inside the wagon rushed to save the vendor, pulling her and her goods inside. The collective struggle to reclaim public spaces has emboldened women, many of whom now proclaim, “I have become braver.”
But the Mahsa movement has not been limited to women’s rights alone. The movement initially protested against mandatory hijab but, like an umbrella, it now encompasses a range of other issues in Iran, including the unbearable economic challenges and ethnic and religious discrimination. Protesters have also been calling for the overthrow of the Islamic Republic. Yet, the state’s brutal suppression of these protests underscores the complexity of achieving political goals such as regime change. According to Jack Goldstone, a scholar of social movements, the Mahsa movement continues to lack some of the key factors needed for a full-scale revolution, such as an organised programme and the involvement of older generations.
The conflict between Iranian authorities and Iranian women dates back to the establishment of the Islamic Republic in 1979, when women’s rights were among the first to be compromised. Women did come to the streets to protest against the enactment of the compulsory hijab law and abrogation of the family protection law in March 1979—but the state prevailed in curtailing women’s rights. Four decades later, despite various policies, ideological education, and unequal laws aimed at curbing their economic, social, and political opportunities, Iranian girls and women are trying to break free from traditional gender roles.
What is undeniable today is the Iranian women’s desire for both “freedom” and an “ordinary life.” These two desires resonate strongly in my conversations with many Iranian women from around the country. Iranian women have made strides in education despite numerous obstacles. They are rising against gender-based oppression and have exhibited remarkable resilience in their quest. However, their economic participation remains disproportionately low, forcing many into the informal economy. Women are also denied the right to run for president, and the majority are disqualified to run for public office.
The Iranian state has persistently attempted to exclude women from various spheres, yet they persist in resisting. They aspire to careers as diverse as football referees, aerospace engineers, mathematicians, musicians, and much more. The evolving lifestyle of ordinary women highlights the failure of the Islamic Republic’s discourse in imposing gender roles. Their fight for the freedom to choose how they dress is just one aspect of the broader rights they seek. According to political scientist Fatemeh Sadeghi, the actions of Iranian women are not rooted in anger. Rather, they represent the transformation of anger into a force for change. Accordingly, political change, in their view, will emerge from social empowerment. These women are, in essence, revolutionaries without a revolution. They do not want to achieve freedom through revolution. They aim to achieve revolution through freedom.
Photo: Rouzbeh Fouladi
As Iran Sells More Oil to China, the U.S. Gains Leverage
A new report, citing data from Kpler, an analytics company, claims that Iranian oil exports to China will reach 1.5 million barrels per day this month, the highest level in a decade.
A new report from Bloomberg, citing data from Kpler, an analytics company, claims that Iranian oil exports to China will reach 1.5 million barrels per day this month, the highest level in a decade. The report has led to a flurry of criticism from hawks that President Biden is failing to enforce U.S. sanctions on Iran’s oil exports and thereby gifting Iran billions of dollars in oil revenue. But in reality, Iran appears unable to spend most of the money—a situation that is giving Biden leverage he can use in future negotations.
Iran’s resurgent oil exports are earning the country a lot of money. The crude oil price is currently hovering at around $80. Iran discounts its oil for Chinese customers, so the actual selling price is probably closer to $74 dollars per barrel. At this price, Iran’s 1.5 million barrels per day of exports are earning the country around $3.3 billion per month.
These back of the envelope calculations are necessary because China’s customs administration stopped reporting the value and volume of oil imported from Iran back in May 2019, when the Trump administration revoked a series of waivers permitting limited purchases of Iranian oil by select countries. When looking to the Chinese data alone, Iran’s export revenue appears much smaller than it is, hiding the true trade balance.
In the most recent three months for which we have customs data, Iran’s imports from China averaged $826 million. In the same period, Iran’s non-oil exports to China averaged $357 million. When not counting Iran’s oil exports, Iran appears to be running a trade deficit with China of around $469 million. But when adding the reasonable estimate of $3.3 billion of oil exports, the monthly trade balance swings dramatically in Iran’s favor. In recent months, Iran has likely run a trade surplus with China of around $2.8 billion per month.
In other words, Iran is earning billions of dollars it appears unable to spend. After all, Chinese goods, especially parts and machinery, are a lifeline for Iranian industry. If Iran was able to buy more Chinese goods, it would be doing so. Two other data points confirm this interpretation. Exports from the UAE to Iran remain depressed, so Chinese goods are not arriving in Iran indirectly. Purchasing managers’ index data for the manufacturing sector also indicates that Iranian firms continue to struggle with low inventories of raw materials and intermediate goods. Moreover, Iran is continuing to doggedly pursue the release of its frozen assets, including $6 billion that will be made available for humanitarian trade as part of the recent U.S.-Iran prisoner deal. Iran would not be so desperate to strike such deals were its oil revenues in China readily accessible. In short, Iran is selling its oil and earning money, but it is not getting the full economic benefit from the surge in oil exports.
Chinese exporters and their banks remain wary of trading with Iran, where entities and whole sectors remain subject to U.S. secondary sanctions. For most Chinese multinational companies, trading with Iran is not worth the risk. In the first six months of this year, Chinese exports to Iran averaged $898 million per month. Exports remain 35% lower than in the first six months of 2017, the most recent year during which Iran enjoyed sanctions relief.
It remains to be seen whether Iran can sustain this new, higher level of oil exports. Oil markets can be fickle, and China’s economic wobbles could depress demand. But for now, Iran’s significant trade surplus with China also means that its renminbi reserves must be growing. This is a novel situation. Historically Iran has run a small trade surplus with China. Between January 2012, when the Obama administration launched devastating financial and energy sanctions on Iran, and January 2016, when the implementation of the nuclear deal granted Iran significant sanctions relief, the average monthly trade surplus was just $511 million (China’s purchases of Iranian oil are reflected in customs data for this period). In other words, assuming its oil revenues are stuck in China, Iran’s reserves are now growing four times faster than in that period.
At first glance, this might look like a major failure for the Biden administration. Biden purposefully maintained the “maximum pressure” sanctions imposed by Trump in an effort to sustain leverage for negotiations and Iranian oil exports remain subject to U.S. secondary sanctions. But those who claim that Biden is failing to enforce his sanctions are failing to see the wisdom of the current U.S. enforcement posture.
First, Biden is loath to deepen already heightened tensions with China. Sanctioning Chinese refiners for their purchases of Iranian oil, thereby targeting China’s energy security, would be a dramatic escalation in the growing economic competition between Washington and Beijing. Second, such escalation would be entirely pointless given the circumstances around Iran’s oil exports—namely that Iran is not getting the normal economic benefits. Given that Iran is earning more money but cannot spend it, the U.S. is actually gaining leverage for future negotiations.
Unlike Trump, Biden has made a serious effort to engage in nuclear diplomacy with Iran and is likely to continue those efforts if there is a reasonable opportunity to achieve a new diplomatic agreement that contains Iran’s nuclear program. But U.S. negotiators have struggled to make a compelling offer to their Iranian counterparts. Many Iranian policymakers felt the promised economic uplift of sanctions relief would be too small. Iran’s opening gambit in the negotiations with Biden included the claim that sanctions had inflicted $1 trillion of damage to Iran’s economy and that Iran was owed compensation.
With its oil exports significantly depressed, Iran has been unable to significantly grow its foreign exchange reserves, which the IMF estimates at around $120 billion. If Iranian officials believe that they need to remediate $1 trillion of economic damage, the windfall represented by the unfreezing of foreign exchange reserves does not count for much.
The longer the sanctions remain in place, the more money will be needed to undo the cumulative effects of U.S. sanctions, which have now hobbled Iran’s economy for over a decade. It is politically impossible for Biden to promise any kind of compensation for Iran—the best that the U.S. can do is promise to once again unfreeze Iran’s own money as part of a new diplomatic agreement.
For this reason, it is a good thing if Iran’s reserves are growing. Iran’s oil exports to China are kind of like payments made as part of a deferred annuity insurance contract. One day, Iran will be able to cash out on that policy. But it can only cash out if it meets the conditions set by the U.S. In other words, every barrel of oil Iran is currently selling to China is increasing U.S. leverage for future talks. It would be wise to let the oil flow.
Photo: Canva
Iran Paid for Su-35 Jets, But Russia Won’t Deliver Them
Earlier this month, Brigadier General Hamid Vahedi, Iran’s air force commander, ended weeks of speculation about the imminent delivery Russian Sukhoi Su-35 fighter jets.
Earlier this month, Brigadier General Hamid Vahedi, Iran’s air force commander, ended weeks of speculation about the imminent delivery Russian Sukhoi Su-35 fighter jets. “Regarding the purchase of Su-35 fighter jets [from Russia], we need them, but we do not know when they will be added to our squadron. This is related to the decision of [Iran’s] high-ranking officials,” he stated in an interview on state TV.
Vahedi's comments sparked speculation about dysfunction in the Russia-Iran partnership, including that Israel had successfully convinced Russia to postpone delivery of the advanced fighter jets to Iran.
While officials in Tehran continue to pursue a partnership with Russia, it is increasingly clear that Russian officials see their relationship with Iran as little more than a card that can be played according to their needs.
Russia’s potential sale of Su-35 jets to Iran has been connected to the deeper military cooperation between the two countries since the Russian invasion of Ukraine in February 2022. Iranian drones are being used by Russian forces to bomb Ukrainian cities. The first drones were transferred from Iran to Russia around one year ago.
But Iran has been waiting for far more than a year to receive the Su-35, which would prove a major upgrade in capabilities for Iran’s aging air force, largely comprised of American jets in service since before the 1979 revolution.
According to one current and one former diplomat with direct knowledge of the matter, Iran made “full payment” for 50 Su-35 fighter jets during the second term of President Hassan Rouhani. The officials requested anonymity given the sensitivity of Iran’s arms purchases. According to the former diplomat, at the time of purchase Russia had promised to deliver the Su-35s in 2023. Neither source expects that the deliveries will be made this year.
A third source, a security official, speaking on background, expressed disappointment that Vahedi’s “uncoordinated interview” had called attention to the fact that the deliveries were now in doubt. Iranian officials feel embarrassment over Russia’s failure to adhere to commitments.
The delay in the delivery could be traced to the strong relationship between Russia and Israel. In June, Axios reported that Israeli officials confronted Russian counterparts over Russia’s growing military cooperation with Iran and the possibility of Russia providing Iran advanced weapon systems. Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu disclosed the “open and frank” dialogue with Russian officials in a closed-door hearing with Israeli lawmakers on June 13.
In the view of the former diplomat, due to their arrogance, Iranian hardliners “fell into the trap” of believing that they were an equal partner to Russia, simply because “the Russians are queuing up to buy arms from them.”
The drone transfers have contributed to Iran’s political isolation, giving Western officials the impression of deepening cooperation between Russia and Iran, even as the Iranian Foreign Ministry continues to claim that Iran remains a neutral party in the Ukraine war. According to the security official, neutrality remains the consensus position of the Iran’s Supreme National Security Council, but he warned that country’s military brass may not all share that same view.
Notwithstanding the ambitions of Iranian generals, Russia continues to treat Iran far worse than an ally. Earlier this week, Russia issued a joint statement with the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), affirming the United Arab Emirate’s claims on three Iranian islands: the Greater Tunb, the Lesser Tunb, and Abu Musa. The statement enraged Iranian officials. Ali Akbar Velayati, a senior advisor to Iran’s Supreme Leader, called Russia’s assent to the statement “a move borne of naivety.” Iran’s foreign minister and its government spokesperson stressed in statements that Iran will not tolerate claims on the three islands from any party. The officials had made such statements before—a China-GCC joint statement from December 2022 caused a similar public outcry.
As Iranian officials are forced to defend their ties with Russia once again, a question remains. Why does Iran have so little leverage over Russia, even after the Russian invasion of Ukraine? The answer lies in the mindset of Iranian officials.
Back in May, Iran’s Supreme Leader, Ali Khamanei, declared that “Dignity in foreign policy means saying no to the diplomacy of begging.” The slogan “diplomacy of begging” has become popular among conservatives and the hardliners, who have used it to condemn the signing of the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) and to accuse former Iranian foreign minister Javad Zarif of begging the West for sanctions relief. But if begging the West for sanctions relief is wrong, why are hardliners eager to beg Russia for the Sukhoi jets?
Tehran’s ties with Moscow were never built on trust. They were built on mutual fears and mutual needs. Were the administration of President Ebrahim Raisi to realize that looking to the West does not preclude political and economic relations with Russia and China, Iran could strengthen its position in the Middle East and regain leverage in its relationship with Russia. Until then, the Russians will continue to look at their relationship with Iran as a nothing more than playing card.
Photo: Wikicommons
Sanctions, CBDCs, and the Role of ‘Decentral Banks’ in Bretton Woods III
In a world with two parallel financial systems, a country would not necessarily have a single reserve bank.
In a recent conversation on the Odd Lots podcast, Zoltan Pozsar offered an interesting use case for central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), a potentially transformative technology that 86 percent of central banks are “actively researching” according to a BIS survey from 2021.
Pozsar, a former Credit Suisse strategist who is setting up his own research outfit, believes that a new global monetary order is emerging—he calls it “Bretton Woods III.” As part of this order, the adoption of CBDCs will enable central banks to play a more pivotal role in global trade through the formation of a “state-to-state” network that is intended to be independent of Western financial centres and the dollar. In this network, central banks will play a “dealer” role when it comes to providing liquidity for trade among developing economies. Commenting on China’s push to internationalise the renminbi, Pozsar set out his vision:
You need to imagine a world where five, ten years from now we are going to have a renminbi that’s far more internationally used than today, but the settlement of international renminbi transactions are going to happen on the balance sheets of central banks. So instead of having a network of correspondent banks, we should be thinking about a network of correspondent central banks and a world where you have a number of different countries and in which each of those different countries have their banking systems using the local currency but when country A wants to trade with country B… The [foreign exchange] needs of those two local banking systems are going to be met by dealings between two central banks.
In short, Pozsar believes that the adoption of CBDCs will enable the creation of a “new correspondent banking system” built around central banks. But even if central banks do begin to use CBDCs to settle trade, reducing dependence on dollar liquidity and legacy correspondent banking channels, the underlying problem motivating CBDC adoption will remain.
Moving away from the dollar-based financial system is foremost about geopolitics. Globalisation, as we have known it, reinforced a unipolar order. The United States was able to leverage its unique position in the global economy into unrivalled superpower status. In the last two decades, the weaponisation of the dollar further augmented U.S. power—Americans are uniquely able to wage war without expending military resources, which is another kind of exorbitant privilege. As Pozsar notes, the countries moving fastest towards CBDCs are those that are either currently under a major U.S. sanctions program (Russia, Iran, Venezuela etc.) or at risk of being targeted (China, Pakistan, South Africa etc.) These countries recognise “that it is pointless to internationalise your currency through a Western financial system… and through the balance sheets of Western financial institutions when you basically do not control that network of institutions that your currency is running through.” As Edoardo Saravalle has argued, the power of U.S. sanctions is actually underpinned by the central role of the Federal Reserve in the global economy.
Adopting CBDCs would enable countries to reduce the proportion of their foreign exchange reserves held in dollars while also reducing reliance on U.S. banks and co-opted institutions such as SWIFT to settle cross-border payments. However, even if countries reduce their exposure to the dollar-based financial system in this way, U.S. authorities will still be able to use secondary sanctions to block central banks from the U.S. financial system for any transaction with a sanctioned sector, entity, or individual. Any financial institution still transacting with a designated central bank could likewise find itself designated.
Moreover, even if Bretton Woods III emerges, leading to the formation of a robust parallel financial system that is not based on the dollar, central banks will continue to engage with the legacy dollar-based financial system. It is difficult to image a central bank correspondent banking network in which nodes are not shared between the dollar-based and non-dollar based financial networks. As such, the threat of secondary sanctions or being placed on the FATF blacklist—moves that would cut a central banks access to key dollar-based facilities—will remain a significant threat.
Even Iran, which is under the strictest financial sanctions in the world, including multiple designations of its central bank, continues to depend on dollar liquidity provided through a special financial channel in Iraq. A significant portion of Iran’s imports of agricultural commodities continue to be purchased in dollars. Iran earns Iraqi dinars for exports of natural gas and electricity to its neighbour. The Iraqi dinars accrue at an account held at the Trade Bank of Iraq. The dinar is not useful for international trade, and so Iran converts its dinar-denominated reserves into dollars to purchase agricultural commodities—a waiver issued by the U.S. Department of State permits these transactions. The dollar liquidity is provided by J.P. Morgan, which plays a key role in the Trade Bank of Iraq’s global operations, having led the creation of the bank after the 2003 invasion.
The fact that the most sanctioned economy in the world depends on dollar liquidity for its most essential trade suggests that central banks will remain subject to U.S. economic coercion, owing to continued use of the dollar for at least some trade. But even in cases where Iran conducts trade without settling through the dollar, U.S. secondary sanctions loom large.
For over a decade, China has continued to purchase large volumes of Iranian oil in violation of U.S. sanctions, paying for the imports in renminbi. Iran is happy to accrue renminbi reserves because of its demand for Chinese manufactures. But owing to sanctions on Iran’s financial sector, Iranian banks have struggled to maintain correspondent banking relationships with Chinese counterparts. When the bottlenecks first emerged more than a decade ago, China tapped a little-known institution called Bank of Kunlun to be the policy bank for China-Iran trade.
The bank was eventually designated by the US Treasury Department in 2012. Since then, Bank of Kunlun has had no financial dealings with the United States, but that has not eased the bank’s transactions with Iran. Bank of Kunlun is owned by Chinese energy giant CNPC, an organisation with significant reliance on U.S. capital markets. When the Trump administration reimposed secondary sanctions on Iran in 2018, Bank of Kunlun informed its Iranian correspondents that it would only process payment orders or letters of trade in “humanitarian and non-sanctioned goods and services,” a move that was intended to forestall further pressure on CNPC. Ultimately, Bank of Kunlun had far less exposure to the U.S. financial system that China’s own central bank ever will, a fact that points to the limits of a central bank correspondent banking network. For CBDCs to serve as a defence against the weaponised dollar, they would need to be deployed by institutions that maintain no nexus with the dollar-based financial system. It is necessary to think beyond central banks.
What Pozsar has failed to consider is that in a world with two parallel financial systems, a country would not necessarily have a single reserve bank. Alongside central banks, we can envision the rise of what I call decentral banks. If a central bank is a monetary authority that is dependent on the dollar-backed financial system and settles foreign exchange transactions through the dollar, a decentral bank is a parallel authority that steers clear of the dollar-backed financial system and settles foreign exchange transactions through CBDCs. The extent to which Bretton Woods III really represents the emergence of a new bifurcated global monetary order depends not only on the adoption of CBDCs, but also the degree to which the innovations inherent in CBDCs enable countries to operate two or more reserve banks whose assets and liabilities are included in a consolidated sovereign balance sheet.
Again, Iran offers an interesting case study for what this innovation might look like. The reimposition of U.S. secondary sanctions on Iran in 2018 crippled bilateral trade between Europe and Iran. Conducting cross-border financial transactions was incredibly difficult owing to limited foreign exchange liquidity and the dependence on just a handful of correspondent banking relationships. France, Germany, and the United Kingdom took the step to establish INSTEX. As a state-owned company, INSTEX would work with its Iranian counterpart, STFI, to establish a new clearing mechanism for humanitarian and sanctions-exempt trade between Europe and Iran. The image below is taken from a 2019 presentation used by the management of INSTEX to explain how trade could be facilitated without cross-border financial transactions.
The model is strikingly like Pozsar’s suggestion that CBDCs will enable central banks to settle trades using their balance sheets, rather than relying on the liquidity of banks and correspondent banking relationships. INSTEX and STFI were supposed to net payments made by Iranian importers to European exporters with payments made by European importers to Iranian exporters, using a “virtual currency unit” to book the trade. The likely imbalances would be covered by a cash injection into INSTEX (Europe was exporting far more than it was importing after ending purchases of Iranian oil). It was an elegant solution, which sought to scale-up the methods being used by treasury managers at multinational companies operating in Iran to purchase inputs and repatriate profits.
Earlier this year, INSTEX was dissolved. Its shareholders, which eventually counted ten European states, lacked the political fortitude to see the project through. Notwithstanding bold claims about preserving European economic sovereignty in the face of unilateral American sanctions, there was always a sense among European officials that Iran was undeserving of a special purpose vehicle. But as the world moves to a new financial order, more institutions like INSTEX will emerge. Pozsar’s vision is bold insofar as he believes central banks will establish new cross-border clearing mechanisms based on CBDCs. But if new digital currencies can emerge to displace the dollar in the global monetary order, so too can new institutions be established.
Pozsar’s vision for Bretton Woods III becomes more convincing if one considers that the emergence of institutions such as decentral banks could lead to the creation of correspondent banking networks that are truly divorced from the dollar-based financial order. However, there remain plenty of reasons to doubt that such a system will emerge. Pozsar appears to have given little consideration to the issue of state capacity. Most countries have poorly managed central banks as it is—in the Odd Lots interview he pointed to Iran and Zimbabwe as early movers on CBDCs. We should have low expectations for the ability of most governments to develop and implement new technologies such as CBDCs or to establish wholly new institutions such as decentral banks. Moreover, the ability of the U.S. to use carrots and sticks to interfere with those efforts should not be underestimated.
There may be compelling structural drivers for something like Bretton Woods III, namely the rise of China and the overall shift in the global distribution of output. But somewhere along the way those structural drivers need to be converted into institutional processes. Bretton Woods is shorthand for the idea that monetary rules are as important for the operation of the global economy as the macroeconomic fundamentals. Countries reluctant to break the rules will struggle to rewrite them.
Photo: Canva
When it Comes to Middle East Diplomacy, Chinese and European Interests Align
In March, China managed to a broker a détente between Iran and Saudi Arabia, achieving a diplomatic breakthrough that had eluded European governments. But Europe and China have shared interests in the region and there is scope for the two powers to work together to foster further multilateral diplomacy.
A version of this article was originally published in French in Le Monde.
In March, China managed to a broker a détente between Iran and Saudi Arabia, achieving a diplomatic breakthrough that had eluded European governments. But Europe and China have shared interests in the region and there is scope for the two powers to work together to foster further multilateral diplomacy.
Europe and China, which both depend on energy exports from the Persian Gulf, have long relied on the US-led security architecture in the region. But the 2019 attacks on oil tankers in the UAE and oil installations in Saudi Arabia, widely attributed to Iran, were a watershed moment. Shifting US interests and President Trump’s erratic reaction to those attacks forced the Chinese and Europeans to take more responsibility for regional security over the last four years.
In 2020, China presented its idea for regional security in the Persian Gulf, arguing that with a multilateral effort, the Persian Gulf region can become “an oasis of security.” In the time since, the agreement between Saudi Arabia and Iran, signed in March, can be considered an outcome of such efforts.
European governments have also sought to back multilateral diplomacy. France was intent on creating a platform for Tehran and Riyadh to engage in dialogue. President Macron helped launch the Baghdad Conference for Cooperation and Partnership that was held in August 2021. The conference was a unique opportunity to gather countries that had not sat around the same table for years. Officials from Iraq, Iran, Kuwait, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, and the UAE, in addition to Egypt, Jordan, Turkey, and France participated. Oman and Bahrain joined the second gathering which took place last December in Amman, Jordan.
The European Union also expressed its support for the Baghdad process. Joseph Borrell said during the Second meeting that “promoting peace and stability in the wider Gulf region… are key priorities for the EU.” Adding that “we stand ready to engage with all actors in the region in a gradual and inclusive approach.”
The Joint Communication to the European Parliament and the Council on a strategic partnership with the Gulf reflects the EU’s keenness on expanding its engagements with the region, particularly on economic ties. The partnership is focused on the GCC, but it mentions that “involvement of other key Gulf countries in the partnership may also be considered as relations develop and mature”—a reference to Iran and Iraq.
Clearly, China and the European Union have multiple areas of mutual concern in the Persian Gulf region. Ensuring freedom of navigation, the undisrupted flow of oil and gas from the region, and non-proliferation of nuclear weapons are shared priorities. But while China is now a central player in the strategic calculations of all states in the region, the Europeans are being largely left out.
European diplomatic outreach has faltered in the face of new political pressures arising from Iran’s continued nuclear escalations, its involvement in Russia’s war against Ukraine, and its repression of ongoing protests for democratic change.
The French president was coincidently in China when the Beijing Agreement was signed, and he welcomed the rapprochement between Saudi Arabia and Iran. Given shared interests, European officials must now find ways to engage with Chinese counterparts on fostering greater regional diplomacy in the Persian Gulf.
There are reports that a regional summit will take place in Beijing later this year, involving all GCC states, Iran and Iraq. This is an important opportunity for multilateral dialogue and cooperation. European governments should consult with regional players and China to secure a seat at the meeting. The EU can help regional countries find ways to jointly tackle basic issues that have impeded economic growth which have resulted in spillover effects such as increased food insecurity and inability to mitigate the rising challenges of climate change.
In parallel, the Baghdad Conference could emerge as an EU-backed platform for economic cooperation in tandem to the now ongoing political and security dialogue process in China. The EU can draw in regional countries to help with reconstruction efforts in Iraq, a country that is in dire need of foreign investment. Given the shuttle diplomacy conducted by Iraqi officials between Iran and Saudi Arabia, and considering the role of France and the EU in the Baghdad conference, it would be apt to explore EU-supported joint economic projects in Iraq, especially those projects that create mutual economic interests between Iran and Saudi Arabia.
Whether in Baghdad, Amman, or Beijing, inclusive regional gatherings are needed to address common economic challenges facing all eight countries surrounding the Persian Gulf. Europe can make significant contributions towards regional dialogue on economic integration by helping to create multilateral platforms, transfer knowhow and technology, and provide financial support. These are areas where China has significantly increased its activities, but European countries enjoy far greater experience in establishing the institutions and infrastructure needed for regional economic development. European officials can leverage this experience to support regional diplomacy. Such efforts would also cement European regional influence at a time when US influence may be waning.
The newly appointed EU Special Representative for Gulf Affairs, Luigi Di Maio, should directly oversee and coordinate initiatives in support of economic diplomacy and integration in the region, finding common ground with China to head off competition. Achieving security through stronger diplomacy and deeper economic ties represents a transformative goal that the region can rally around.
Photo: IRNA